Study Fig. 6.1, which shows the employment structure of Germany (an MEDC) and Egypt (an LEDC) in 1960, 1985 and 2010.

Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 6.1, which shows the employment structure of Germany (an MEDC) and Egypt (an LEDC) in 1960, 1985 and 2010.

Did this page help you?
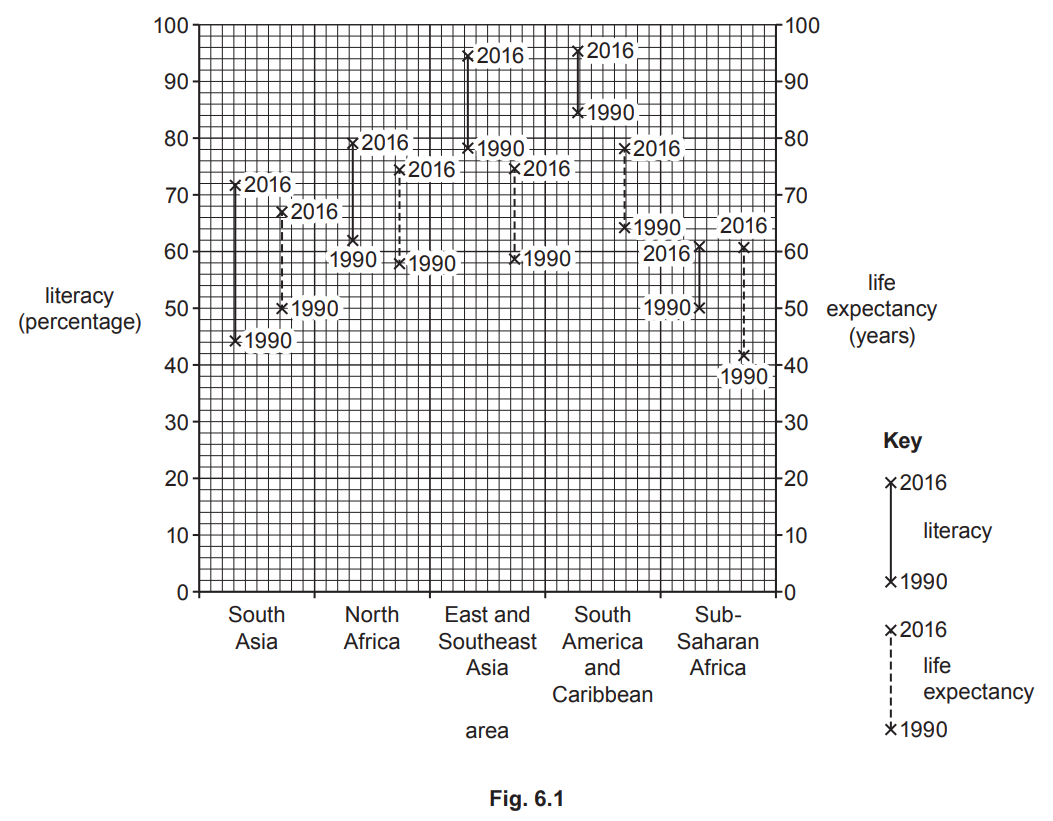
Study Fig. 6.1, which shows information about two indicators of development, literacy and life expectancy, in five parts of the world.
[1]
(ii) Identify the following from Fig. 6.1:
- the area with the highest life expectancy in 1990
- the increase in the literacy percentage in South Asia between 1990 and 2016.
........................ %
(iii) Explain why life expectancy varies in countries at different levels of economic development.
[3]
(iv) State two other indicators of development. For each one, explain why it is a useful indicator of the level of development of a country.
Indicator 1 .........................................................................................................................
Indicator 2 .........................................................................................................................
[4]
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.1, which is information about the changes in the employment structure of Australia (an MEDC) between 1950 and 2015.
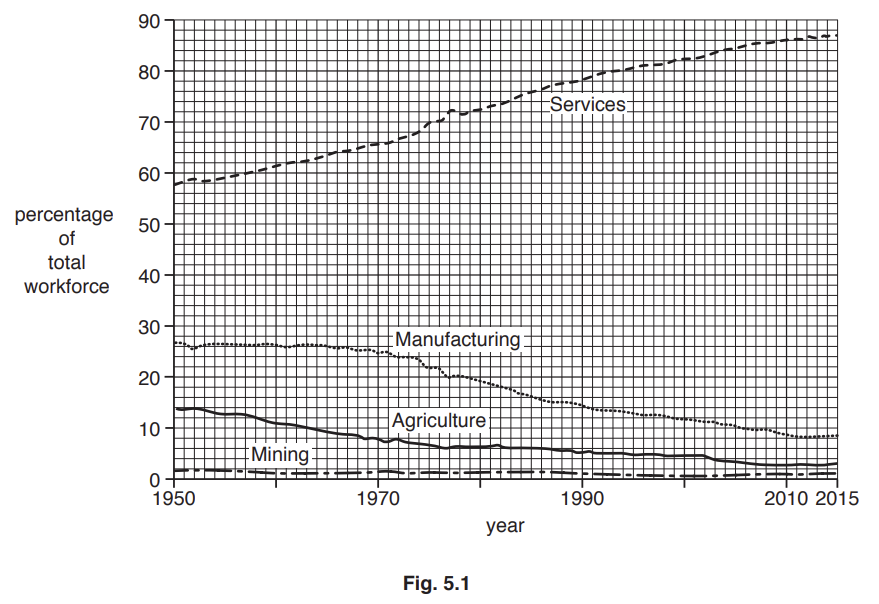
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.1, a map showing the Human Development Index (HDI).

| Brazil | |
| Canada | |
| China | |
| Sudan |
[1]
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.1, which shows information about the employment structure of Cameroon, Italy and Japan.

Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.1, which shows information about the relationship between two indicators of development.

Fig. 5.1
[1]
[2]
[3]
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.2, which shows the Human Development Index (HDI) in different countries in Africa.

Fig.5.2
Using Fig. 5.2 only, compare the distribution of the countries with the highest (over 0.68) and lowest (less than 0.42) HDI within Africa.
[3]
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.1, which shows information about the relationship between two indicators of development.

Fig. 5.1
[1]
[2]
[3]
| tick ( |
|
| All countries with high HDI have small populations. | |
| HDI figures are measured per 1000 of the population. | |
| HDI is a composite indicator of development. | |
| HDI is the same as GDP per person. | |
| HDI scores for every country are between 0 and 1. | |
| Most people who live in a country with a high HDI will be poor. | |
| Many people who live in a country with a low HDI will not have completed secondary education. | |
| The lower the HDI, the shorter the life expectancy is likely to be. | |
| There will be more people per doctor where HDI is higher. |
[4]
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 6.1, which is a map showing the locations of three different factories in an area in Italy (an MEDC in Europe).

Fig. 6.1
[1]
1 ...................................................
2 ...................................................
[2]
[3]
1 ...................................................
2 ...................................................
[4]
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.1, which is a map showing the HDI of Nigeria’s states. Nigeria is an LEDC in Africa.
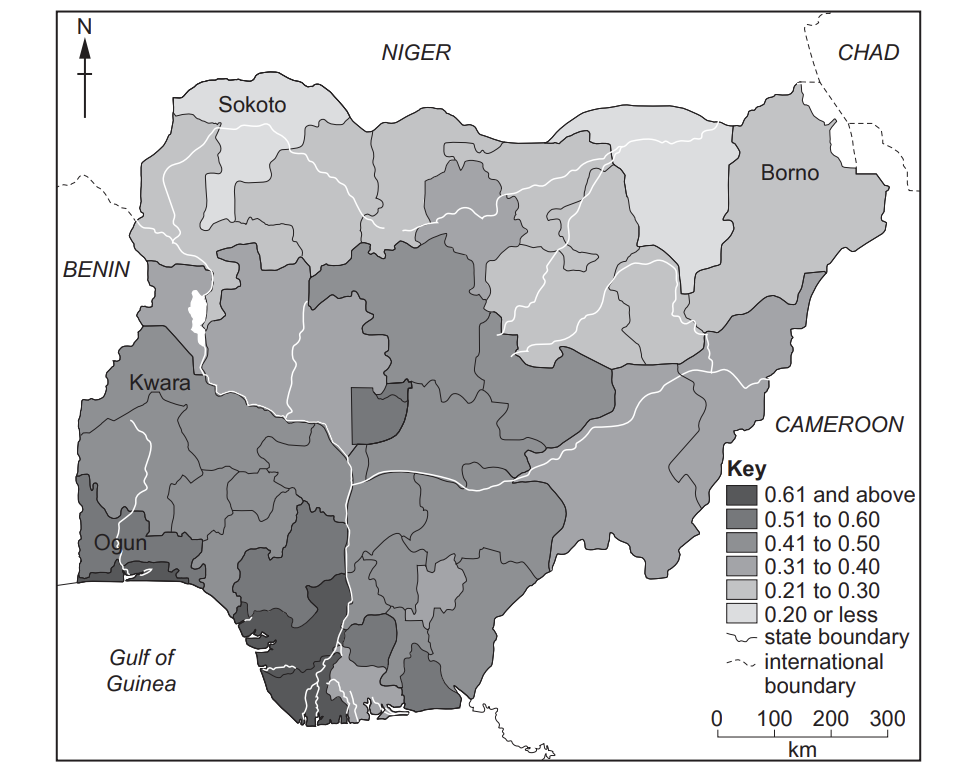
Fig. 5.1
H............................ D............................. I............................
[1]

[2]
Suggest three reasons why some states of Nigeria have a higher HDI than other states.
1 ............................
2 ............................
3 ............................
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.1, which is a diagram showing development indicators for four countries.

[2]
[3]
Did this page help you?
For a named example of a transnational corporation you have studied, describe its impacts at a local and national scale.
Name of transnational corporation .................................................................
Did this page help you?
For a country you have studied, describe the positive and negative impacts of a named transnational corporation being located there.
Name of country ..............................
Name of transnational corporation ..................................
Did this page help you?
For a named transnational corporation (TNC) you have studied, explain why it operates in many countries.
Name of transnational corporation (TNC) ................................................
Did this page help you?
For a named transnational corporation (TNC) you have studied, describe the advantages and disadvantages it brings for people at a local scale.
Name of transnational corporation
[7]
Did this page help you?
Explain the causes of globalisation. You should refer to examples which you have studied.
[7]
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.1, which is a diagram showing development indicators for four countries.

Explain why there may be inequalities in levels of development within a country.
[4]
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.2, which is a table showing information about GDP per person, access to improved water sources and life expectancy in five LEDCs.
GDP per person is a measure of wealth.
| GDP per person (US $) |
access to improved water sources (%) |
life expectancy (years) |
|
| Mexico | 18900 | 96 | 76 |
| Paraguay | 9400 | 98 | 77 |
| Philippines | 7700 | 92 | 69 |
| Thailand | 16800 | 98 | 75 |
| Venezuela | 15100 | 93 | 76 |
Did this page help you?
Study Figs. 5.2, 5.3 and 5.4, which are photographs of different places where people are employed.
(i) For each of Figs. 5.2, 5.3 and 5.4 state the sector of production which is shown.



Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.2, which shows four plans that the government of an LEDC in Africa is considering.
|
Plan 1 Build more schools in rural areas and allow all children up to the age of 16 to attend free of charge. |
|
Plan 2 Build a multi-purpose dam across a major river which flows through the centre of the country. |
|
Plan 3 Offer financial incentives to attract transnational corporations which manufacture electrical goods. |
|
Plan 4 Build one large coastal tourist resort and another resort close to a national park in the mountains. |
Fig. 5.2
[3]
[5]
Did this page help you?
Explain how changes in technology have enabled globalisation to occur.
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.2, which shows indicators of development for selected countries in Africa.
| Country | Life expectancy (years) |
Energy use per person (kg. of oil equivalent) |
Number of doctors (per 100 000 people) |
Adult literacy (percentage) |
| Angola | 55 | 606 | 8 | 67 |
| Egypt | 73 | 735 | 212 | 58 |
| Ethiopia | 61 | 299 | 3 | 43 |
| Kenya | 64 | 494 | 13 | 85 |
| South Africa | 50 | 2587 | 69 | 87 |
| Tanzania | 61 | 465 | 2 | 78 |
| Uganda | 54 | 776 | 5 | 70 |
Fig. 5.2
Country ................................
Justification ....................................
[5]
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.1, a map showing the Human Development Index (HDI).

Explain why there are differences in levels of development between countries.
[4]
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.1, which shows information about the relationship between two indicators of development.

Fig. 5.1
Another indicator of development is employment structure.
Describe the changes in the employment structure of a country as its GDP per person increases.
[4]
Did this page help you?
Study Fig. 5.2, which shows the Human Development Index (HDI) in different countries in Africa.

Fig.5.2
Explain why there are inequalities in wealth between countries.
[5]
Did this page help you?
Study Figs. 5.2, 5.3 and 5.4, which are photographs showing different employment sectors.
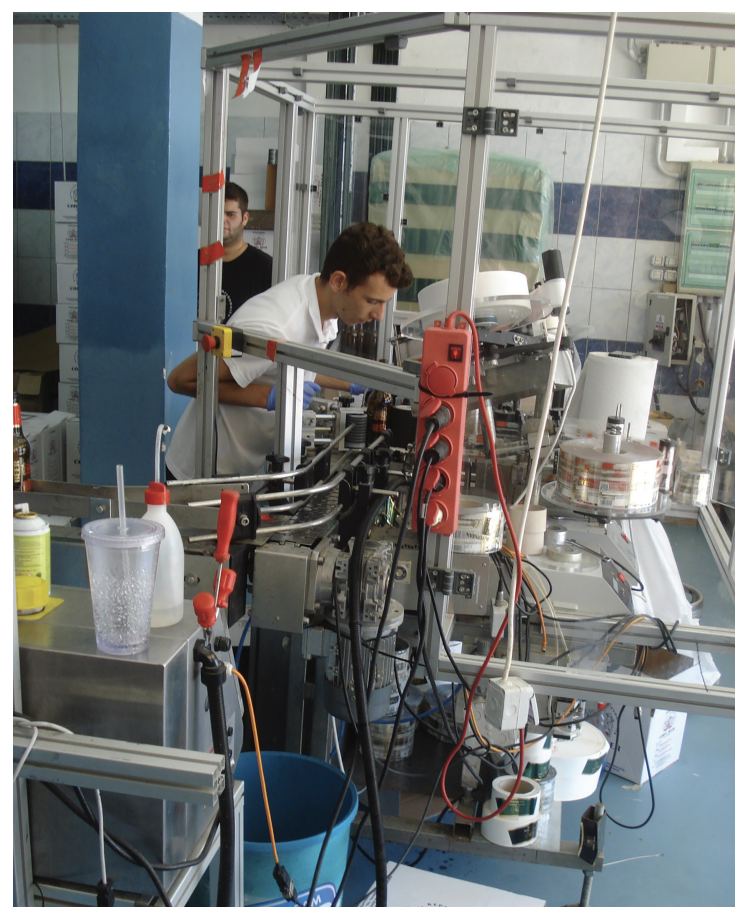 Fig. 5.2
Fig. 5.2 Fig. 5.3
Fig. 5.3
Identify the employment sectors shown in each of Figs. 5.2, 5.3 and 5.4.
Fig. 5.2 .............................................
Fig. 5.3 .............................................
Fig. 5.4 .............................................
[3]
[5]
Did this page help you?