Formulae & Functions
What is the difference between a Formula and a Function?
- A formula can:
- Contain a function
- Be simple calculations/mathematical operation
- Be typed directly into the formula bar
It is a statement that performs calculations on values in your worksheet. For instance, "=A1+B1"
- A function:
- Is a special type of formula/complex formula
- Is built into the software/spreadsheet
- Can be used to simplify complicated calculations
- Can have built-in commands
- Has a pre-defined name/reserved word
- Is a special type of formula/complex formula
It is a preset command in spreadsheets. It is a type of formula that performs specific calculations like SUM, AVERAGE, MAX, MIN, etc. For instance, "=SUM(A1:B1)"
Using Functions
|
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
1 |
10 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
|
2 |
15 |
25 |
35 |
45 |
|
3 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
50 |
- Spreadsheets offer a variety of functions. Some of the most commonly used are:
- E.g. "=SUM(A1:B2)" This would add all the numbers from cell A1 to B2, giving the result 65.
- E.g. "=AVERAGE(A1:B2)" This would find the average of all numbers from cell A1 to B2, giving the result 16.25.
- E.g. "=MAX(A1:B2)" This would return the maximum number in the range from A1 to B2, which is 25.
- E.g. "=MIN(A1:B2)" This would return the minimum number in the range from A1 to B2, which is 10.
- E.g. "=INT(A2)" This would round down the number in cell A2 to the nearest integer, which is 15.
- E.g. "=ROUND(A2, 0)" This would round the number in cell A2 to the nearest whole number, which is 15.
- E.g. "=COUNT(A1:B2)" This would count the number of cells in the range A1 to B2 that contain numbers, which is 4.
- E.g. "=LOOKUP(25, A1:B3)" This would look for the number 25 in the range A1 to B3 and return it.
- E.g. "=VLOOKUP(25, A1:B3, 2, FALSE)" This would look for the number 25 in the first column of the range A1 to B3 and return the corresponding value in the second column of the same row.
- E.g. "=HLOOKUP(25, A1:D2, 2, FALSE)" This would look for the number 25 in the first row of the range A1 to D2 and return the corresponding value in the second row of the same column.
- E.g. "=XLOOKUP(25, A1:B3, D1:D3)" This would look for the number 25 in the range A1 to B3 and return the corresponding value from the range D1 to D3.
- E.g. "=IF(A1>B1, "Yes", "No")" This would check if the value in cell A1 is greater than the value in cell B1. If true, it returns "Yes". If false, it returns "No".
- SUM: Adds all the numbers in a range of cells
- AVERAGE: Calculates the average of a range of cells
- MAX and MIN: Finds the largest and smallest numbers in a range respectively
- INT: Rounds a number down to the nearest integer
- ROUND: Rounds a number to a specified number of digits
- COUNT: Counts the number of cells in a range that contain numbers
- LOOKUP, VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, XLOOKUP: Looks up values in a table based on a given condition
- IF: Returns one value if a condition is true and another if it's false
Using External Data Sources within Functions
- Spreadsheets allow you to use external data sources within functions.
- This could be data from another worksheet, workbook, or even a database
Using Nested Functions
- You can use a function within another function. This is called nesting.
- For instance, "=IF(A1>B1, MAX(A1:B1), MIN(A1:B1))".
- This checks if A1 is greater than B1, and if true, it returns the max value, else it returns the min value
Worked example
Tawara school has a shop that sells items needed by pupils in school. Part of a spreadsheet with details of the items is shown.
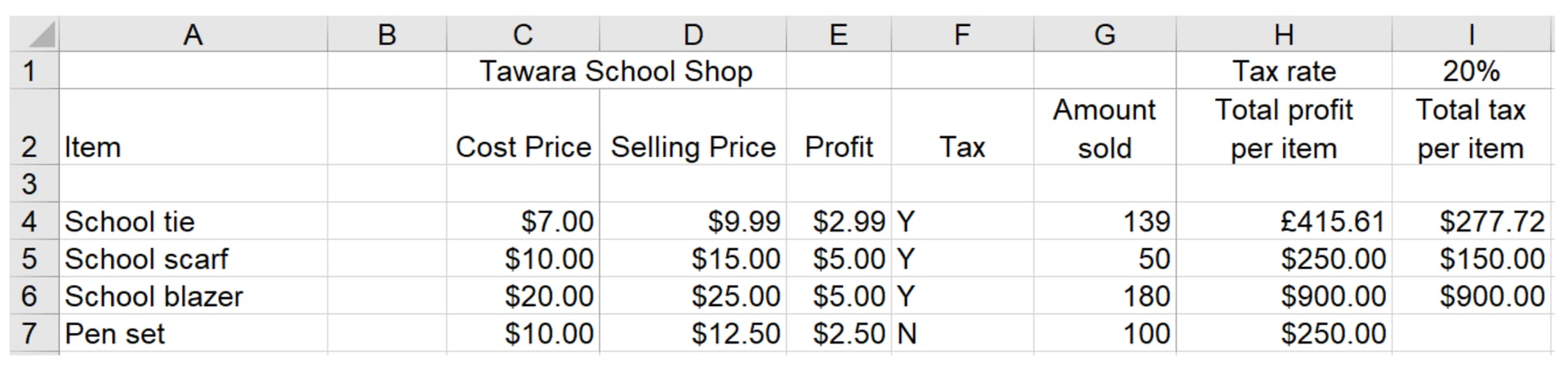
Tax is paid on certain items sold in the shop. The tax rate that has to be paid is 20% of the selling price. If tax is to be paid on an item, then ‘Y’ is placed underneath the Tax heading.
The formula in I4 is: IF(F4=''Y'',($I$1*D4*G4),'''')
Explain, in detail, what the formula does.
[5]
5 of:
If Tax is payable then//If F4 is equal to "Y" then [1]
If true the tax is paid [1]
Multiply the rate of tax/I1 [1]
By the selling price/D4 [1]
By the amount sold/G4 [1]
If Tax is not payable//If F4 <>"Y"//Else//Otherwise [1]
Then display a blank [1]
The tax is not paid [1]
Exam Tip
- If you're asked about a complex formula or function, plan out your answer and work from left to right as you track through the formula. E.g. in the question above IF(F4="Y",($I$1*D4*G4),"") would become If F4 is equal to "Y" then multiply I1 by D4 by G4. If F4<>"Y" then display a blank

