Dismissal & Redundancy
- Dismissal (firing or sacking) is the termination of employment by an employer against the will of the employee
- Employees are usually terminated due to their misconduct (e.g. violating company policy) or poor performance
- The employer may choose to dismiss them immediately (without notice or compensation) or provide a notice period which they can work out
- In some countries, an employee can take the business to court if they feel they were unfairly dismissed
-
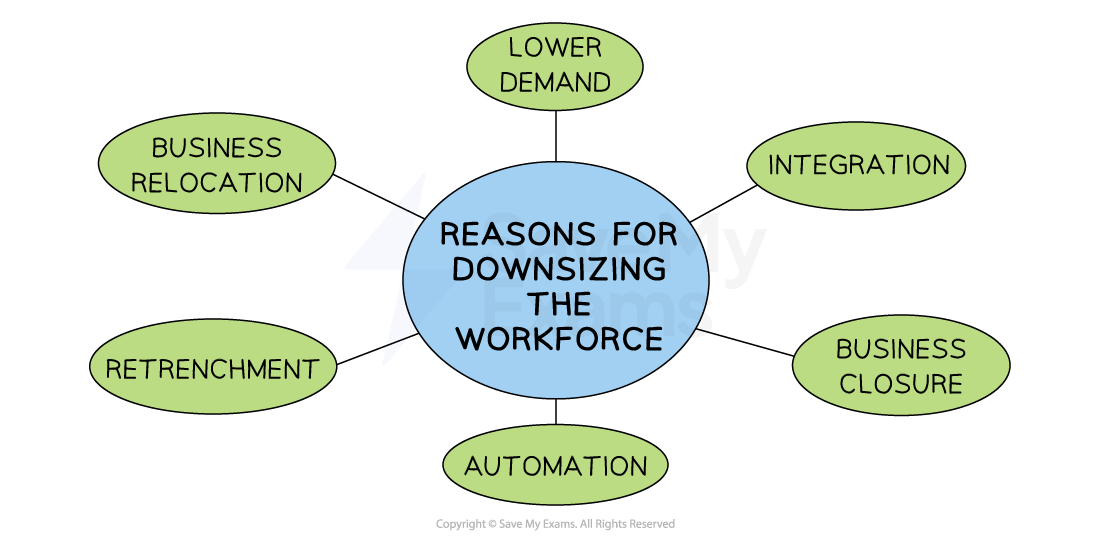
Redundancy is where a job role is no longer needed by a business and a worker is dismissed, usually with compensation
-
The legal process for selecting workers for redundancy must be very clear and fair
-
The Factors used to Determine who is made Redundant
|
Worker Productivity |
Lateness or Absence data |
Length of time Employed |
Workers with Essential Skills |
|
|
|
|
- Some workers are happy to be made redundant
- This may be because they have another job they can go to, they want to retire early or they want to start their own business
-
Some businesses offer a good redundancy 'pay out' which is attractive to workers