Roles, Responsibilities and Organisational Relationships
- The organisational structure of a business determines the roles, responsibilities and relationships in an organisation
- Individuals at the top of the structure usually have more authority
- Middle managers will have relationships with senior managers, other middle managers, and their subordinates
- These hierarchies determine the formal routes through which communication often flows in a business
Diagram to show Possible Business Roles
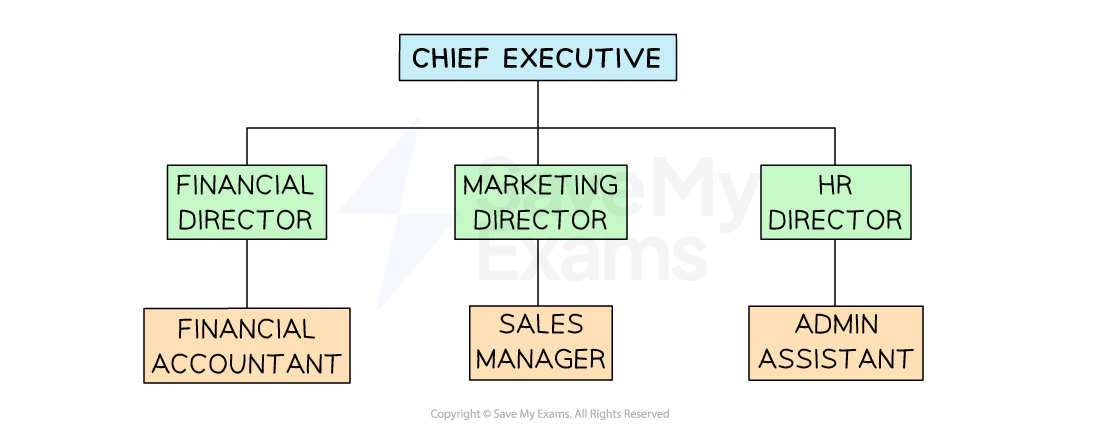
Many larger firms are arranged into functional departments such as Finance and marketing, which are led by directors who carry the final responsibility for the work of everyone in the department
Managers
- Managers have many responsibilities in the business and help it to operate effectively on a day-to-day basis
- Types of managers include directors, line managers and supervisors
Roles and Responsibilities of Managers in an Organisation
Job Roles |
Responsibilities |
|
Owners/Directors |
|
|
Managers |
|
|
Supervisors/Team Leaders |
|


