Introduction to External Sources of Finance
- An external source of finance is money that is introduced into the business from outside
- External finance is used when a business cannot fulfil its needs with internal sources of finance
The main Sources of External Finance
Overdrafts |
Trade Credit |
Loans |
|
|
|
Share Capital |
Venture Capital |
Crowdfunding |
|
|
|
-
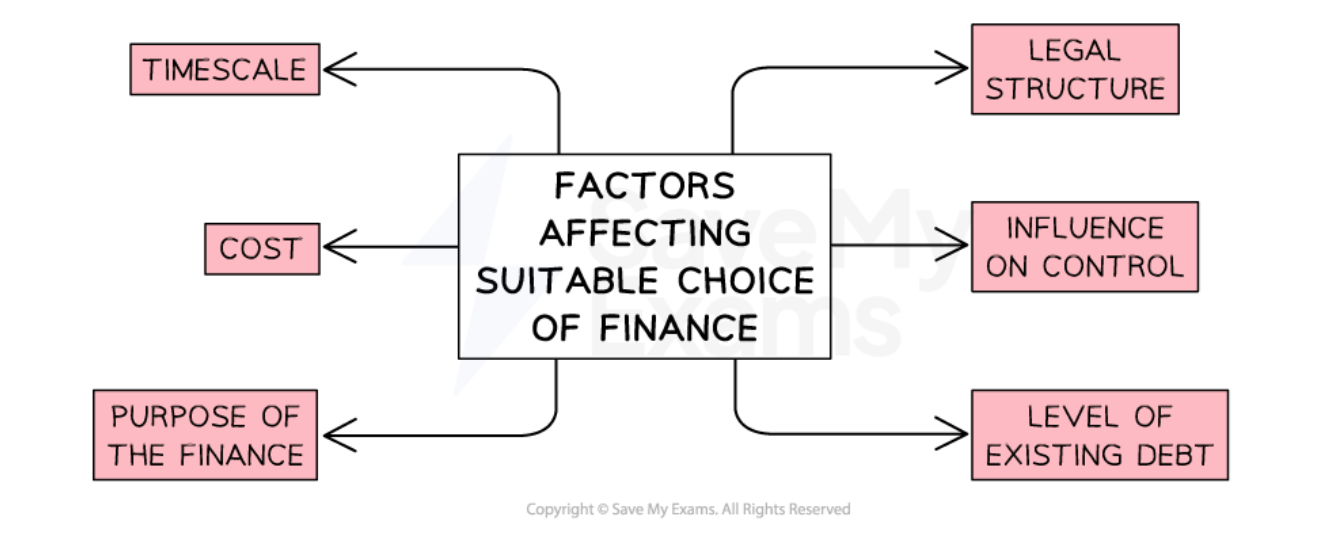
The implications of the different types of external finance need to be carefully considered
-
Interest and fees to arrange finance can vary significantly between financial providers
-
The percentage of company ownership required in exchange for finance depends on how much risk investors are willing to take
-
The length of time allowed to repay borrowings or achieve investment targets also varies
-