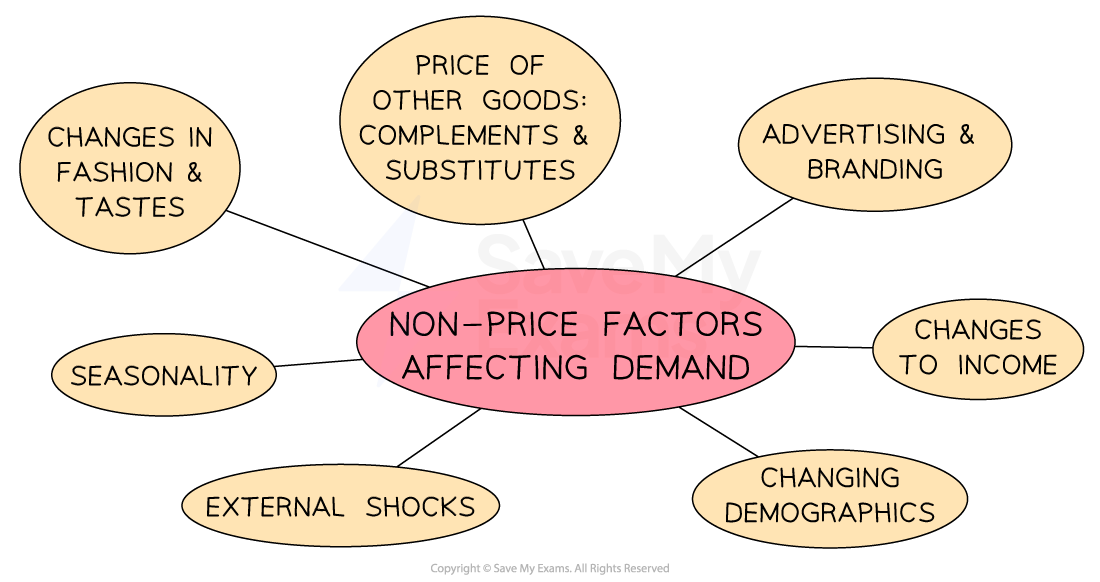
An Introduction to Demand
- Demand refers to the number of goods/services customers are willing to buy at a given price
- Effective demand occurs when customers are willing and able (they have the money) to buy at a given price
- Effective demand occurs when customers are willing and able (they have the money) to buy at a given price
- There is an inverse relationship between the quantity demanded by customers and the price
- As the price increases, the quantity demanded decreases
- As price decreases, the quantity demanded increases
- Hence the demand curve slopes downwards from left to right
- This can be illustrated in the diagram below

A demand curve showing how a change in price will lead to a change in quantity demanded (QD)
Diagram Analysis
- An increase in price from £10 to £15 leads to a movement up the demand curve from point A to B
- Due to the increase in price, the quantity demanded (QD) has fallen from 10 to 7 units
- Due to the increase in price, the quantity demanded (QD) has fallen from 10 to 7 units
- A decrease in price from £10 to £5 leads to a movement down the demand curve from point A to point C
- Due to the decrease in price, the QD has increased from 10 to 15 units
Exam Tip
When writing about a movement along the demand curve we use the term quantity demanded