Group 2 Elements
Reactions with water and oxygen
- The reaction of group 2 metals with oxygen follows the following general equation:
2M (s) + O2 (g) → 2MO (s)
Where M is any metal in group 2
Remember than Sr and Ba also form a peroxide, MO2
- The reaction of all metals with water follows the following general equation:
M (s) + 2H2O (l) → M(OH)2 (s) + H2 (g)
Except for, Be which does not react with water
Group 2 Metals reacting with Water and with Oxygen - Equations
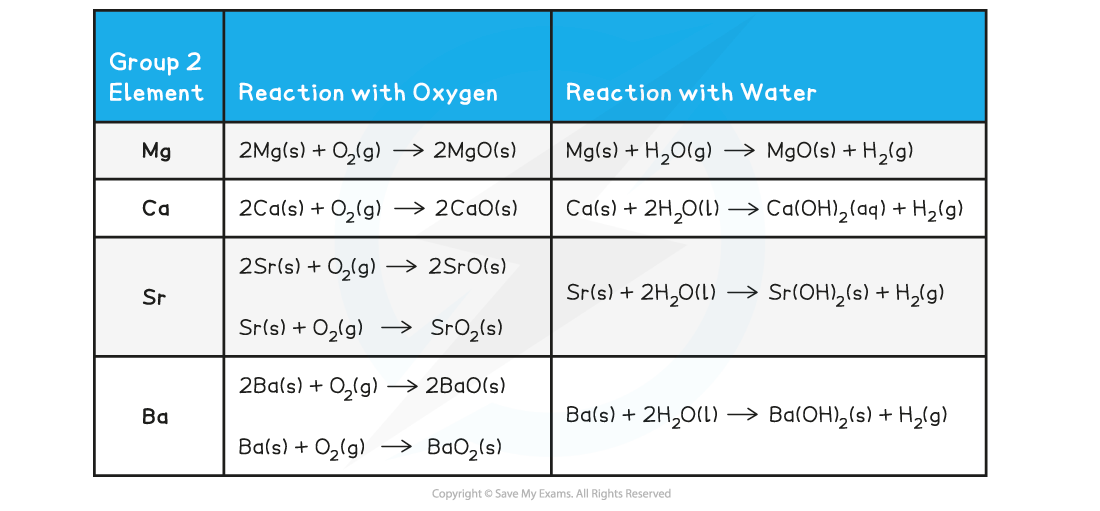
- Magnesium reacts extremely slowly with cold water:
Mg (s) + 2H2O (l) → Mg(OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
- The solution formed is weakly alkaline (pH 9-10) as magnesium hydroxide is only slightly soluble
- However, when magnesium is heated in steam, it reacts vigorously with steam to make magnesium oxide and hydrogen gas:
Mg (s) + H2O (g) → MgO (s) + H2 (g)
Reactions with chlorine
- Group 2 metals react with chlorine gas to give the metal chloride
- For example
Mg (s) + Cl2 (g) → MgCl2 (s)



