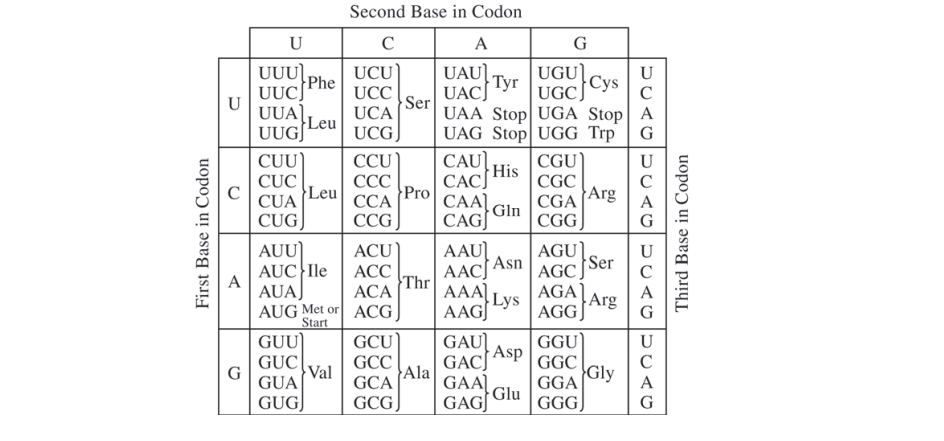
Information flow in cells can be regulated by various mechanisms.
Describe the role of THREE of the following in the regulation of protein synthesis:
- RNA splicing
- repressor proteins
- methylation
- siRNA
Information flow can be altered by mutation. Describe THREE different types of mutations and their effect on protein synthesis.
Identify TWO environmental factors that increase the mutation rate in an organism, and discuss their effect on the genome of the organism.
Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in the phenotype caused by mechanisms other than changes in the DNA sequence. Describe ONE example of epigenetic inheritance.
Did this page help you?