Distribution of Volcanic Hazards
- Most active volcanoes occur at or near plate boundaries
- Many (about 75%) occur around the 'Ring of Fire' surrounding the Pacific Ocean
- Vulcanicity (volcanic activity) is focused on constructive and destructive plate margins
- At constructive margins, eruptions tend to be small and >effusive
- The eruptions are usually basaltic lava:
- Low gas content
- Low viscosity
- Higher temperature
- At destructive margins, eruptions tend to be explosive as the magma is forcing its way to the surface
- These eruptions are often andesitic or rhyolitic lava:
- High gas content
- High viscosity
- Lower temperature
- Volcanoes can also be found at hot spots in the middle of plates, like Hawaii in the central Pacific
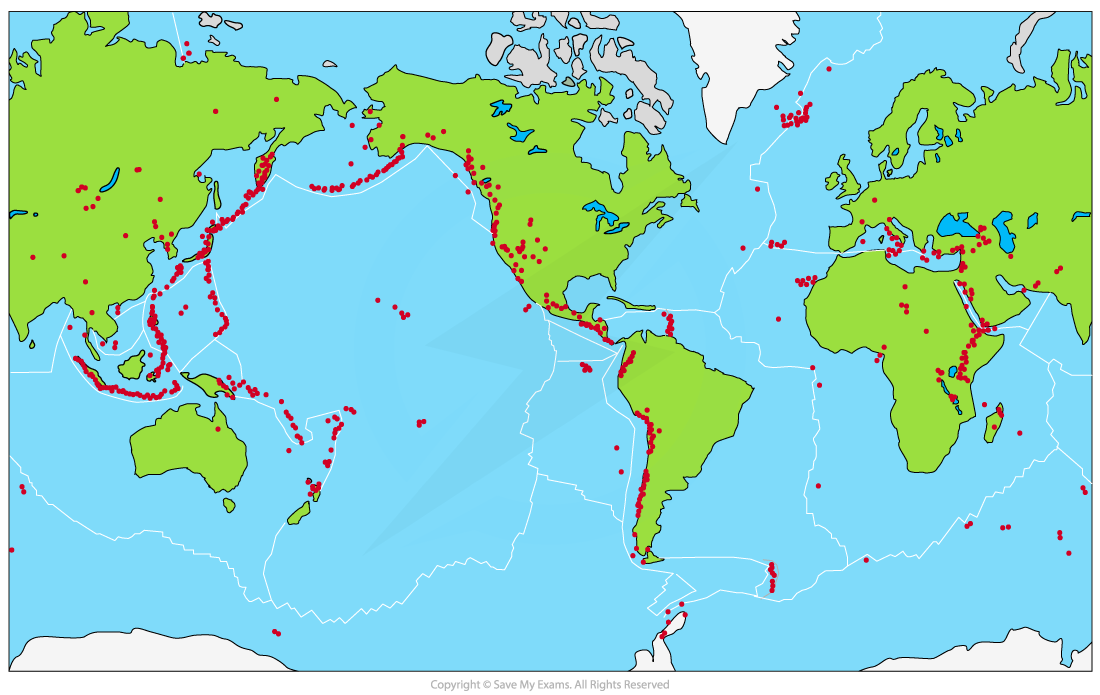
Global distribution of active volcanoes
Exam Tip
It is important that you are confident to describe distribution.
- What is the general pattern?
- Does the pattern relate to anything else for example the location of plate boundaries?
- Are they near the equator or further away?
- Are they inland or coastal?
Use map features to help with your description - place names, compass rose, latitude and longitude


