Communications with Satellites
- Geostationary and polar orbiting (low orbit) satellites are both used for communicating information

Geostationary and polar orbits around the Earth
Geostationary Satellites
- Geostationary satellites orbit above the Earth’s equator
- The orbit of the satellite is 24 hours
- At a height of 36 000 km above the Earth’s surface, much higher than polar satellites
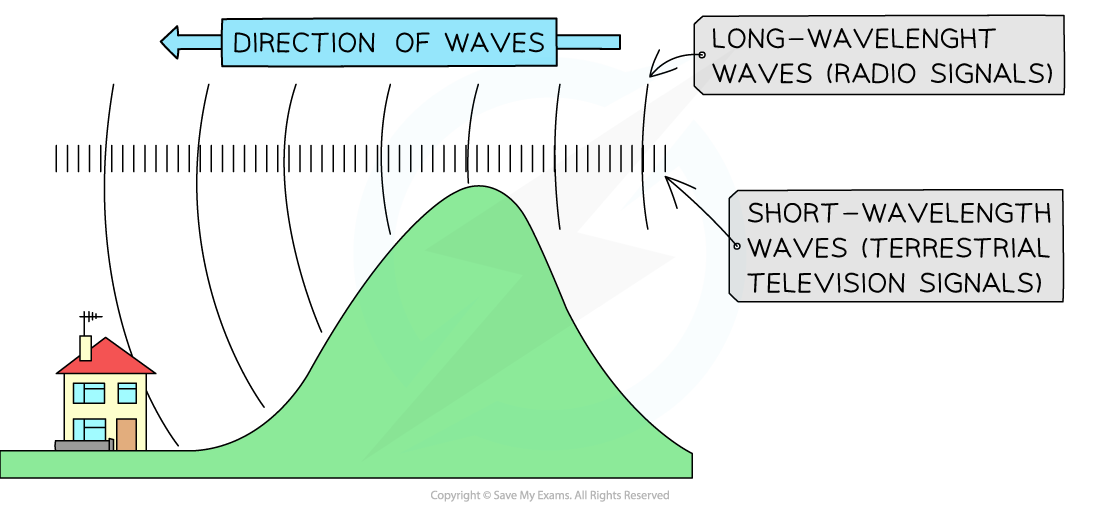
- Used for radio and telecommunication broadcasting around the world due to its high orbit

Some satellite phones and direct broadcast satellite television use geostationary satellites
Polar Satellites
- Polar, or low orbit, satellites orbit around the Earth’s north and south poles
- These orbit much lower than geostationary satellites, at around 200 km above sea level
- Used for monitoring the weather, military applications, and taking images of the Earth’s surface
- There is a much shorter time delay for signals compared to geostationary orbit signals
- The signals and images are much clearer due to the lower orbit
- However, there is limited use in any one orbit because more than one satellite is required for continuous operation

Some satellite phones use low-orbit artificial satellites if a more detailed signal is required