Exact Trig Values
What are the exact values in trigonometry?
- Trigonometry could appear on the non-calculator paper
- You will need to know the following exact values
| Not Defined |
- Note that the values of sin θ going from 0° to 90° match those of cos θ going from 90° to 0°
How are exact trig values for 30° and 60° derived?
- Draw an equilateral triangle where the length of each side is 2
- Each angle will be 60°
- Halve the triangle to form a right-angled triangle where one of the lengths is now 1
- One angle will now be 30°
- Find the length of the missing side using Pythagoras
- Use SOHCAHTOA to find the exact values of the trig ratios for 30° and 60°

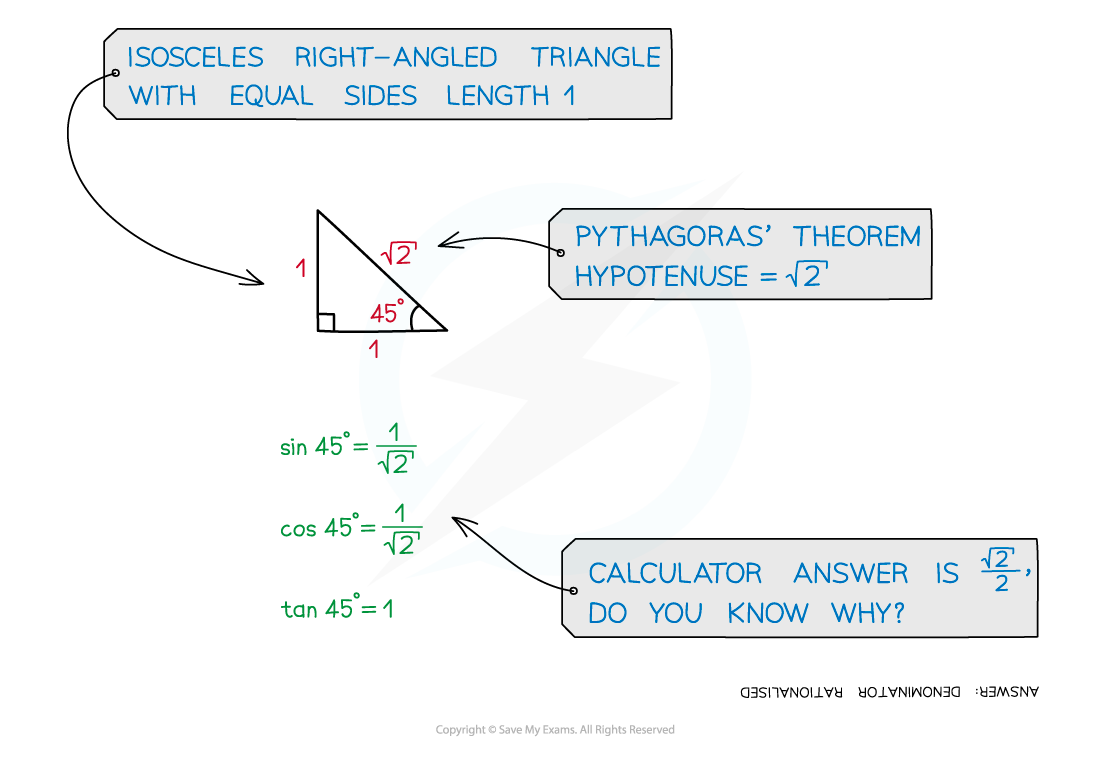
How are exact trig values for 45° derived?
- Draw an isosceles right-angled triangle where the length of the equal sides is 1
- The two equal angles will be 45°
- Find the length of the missing side using Pythagoras
- Use SOHCAHTOA to find the exact values of the trig ratios for 45°
Exam Tip
- If you forget the exact values in your exam
- Use a value that you think it could be
- Even if the value you used is incorrect, you will still get method marks for the rest of the question
Worked example
The following diagram is not drawn to scale.

Without using a calculator, find the value of .
You have the hypotenuse and the side that is adjacent to the angle
Use CAH
Multiply both sides by 24
Use

