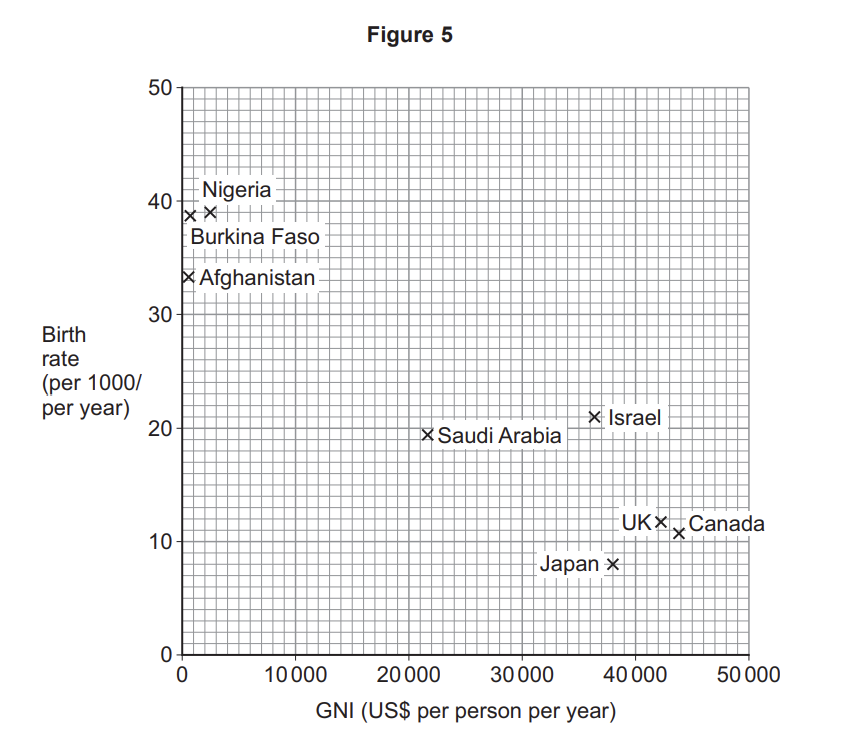
Study Figure 5, a table showing the Gross National Income (GNI) data for selected countries in 2016.
Figure 5
| Country name | GNI US$ per person |
| Argentina | 11 960 |
| Belgium | 41 860 |
| China | 8 260 |
| Finland | 44 730 |
| Haiti | 780 |
| India | 1 680 |
| Kenya | 1 380 |
| Mali | 750 |
| Poland | 12 680 |
| Spain | 27 520 |
| United Kingdom | 42 390 |
Did this page help you?