Changes in the Global Climate (Edexcel GCSE Geography A)
Revision Note

Author
Jacque CartwrightExpertise
Geography Content Creator
Changes in the Global Climate
Climate change is large-scale, long-term changes in average temperatures and weather patterns
The global climate conditions of the Earth change over time, leading to colder and warmer periods
The last 2.6 million years are the Quaternary period, when there have been 60 cold periods and warmer interglacial periods
The last ice age ended approximately 25,000 years ago
Global climate over time

Ice core data: changes in temperature over the last 11,000 years
As well as the historical changes in climate, average temperatures have increased annually since the 1980s

Temperatures continue to rise year on year
The greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is essential to the survival of life on Earth
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere allow thermal radiation from the sun to reach the Earth's surface
These greenhouse gases absorb some of the thermal heat and stop it from radiating out into space
This maintains the Earth's average temperature
Without the greenhouse effect, the average temperature would be -18°C
Greenhouse gases from natural sources
Water vapour: Evaporation from the oceans, seas and plants
Carbon dioxide: Volcanic eruptions, wildfires and respiration
Methane: Emitted from oceans and soils as part of decomposition, termites also emit methane
Nitrous oxide: Soils and oceans
The greenhouse effect

Worked Example
Study the figure, a graph showing variation in average global temperatures, 1880-2017

Which one of the following statements is true?
(1 mark)
A. In the early 1940s, global temperatures were below the 20th century average
B. Global temperatures showed a steady increase between 1940 and 1980
C. The 15 hottest years were all recorded between 1995 and 2017
D. Global temperatures have been above the 20th century every year since 1960
Answer:
C - The 15 hottest years were all recorded between 1995 and 2017 (1)
Causes & Evidence of Natural Climate Change
Causes of Natural Climate Change
Cause | Impact |
|---|---|
Milankovitch Cycles | Long-term changes to the Earth's orbit and position. This changes how much solar radiation the Earth receives The Earth's orbit changes every 100,000 years a more circular orbit leads to cooler periods and an elliptical orbit leads to warmer periods The Earth's tilt varies every 40,000 years and the greater the tilt, the hotter summers are and colder the winters are Every 24,000 years, the Earth wobbles on its axis and this can affect the seasonal temperatures |
Volcanic Eruptions | Large-scale eruptions lead to vast quantities of ash being ejected into the atmosphere Ash in the atmosphere blocks solar radiation, leading to a decrease in temperatures The 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo, Philippines, reduced global temperatures by 1°C in 1992 |
Solar Variation | The Sun goes through 11-year cycles of solar activity that are linked to higher average temperatures Sunspots are areas of intense and complicated magnetic fields that emit solar plasma flares thousands of kilometres above the sun The flare quickly reaches temperatures of 20 million °C and has the same energy as a few million volcanic eruptions on Earth
Sunspots range from Earth-size 'pimples', to swollen scars halfway across the surface of the Sun |
Milankovitch cycles
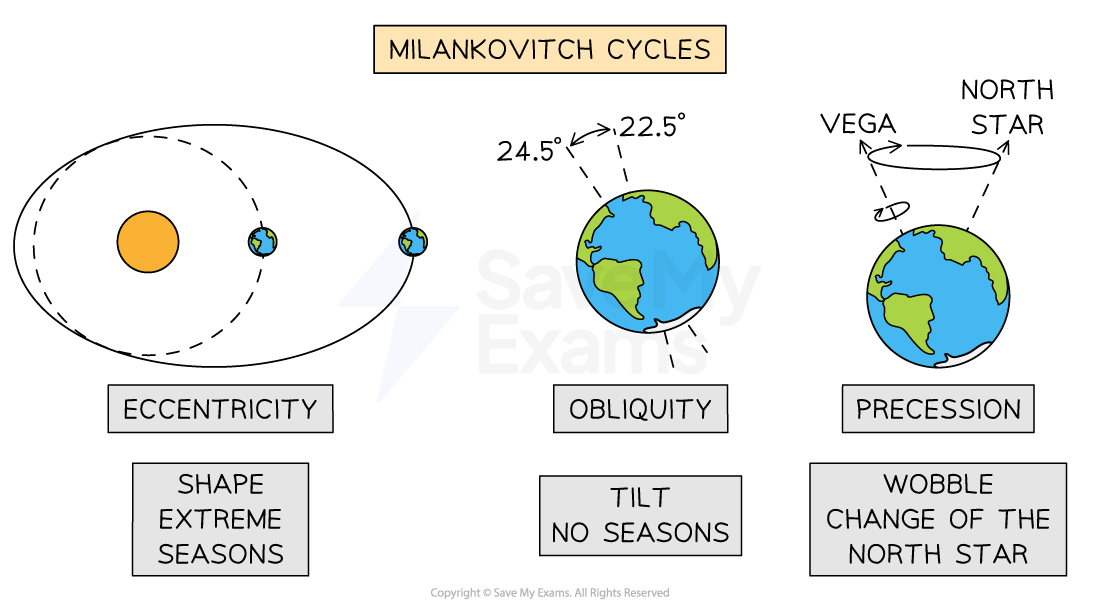
The shape, tilt and wobble of Earth's movement over thousands of years affect long-term climate
Volcanic eruptions

Large-scale eruptions block insolation and reduce temperatures
Ejection of solar plasma from the Sun
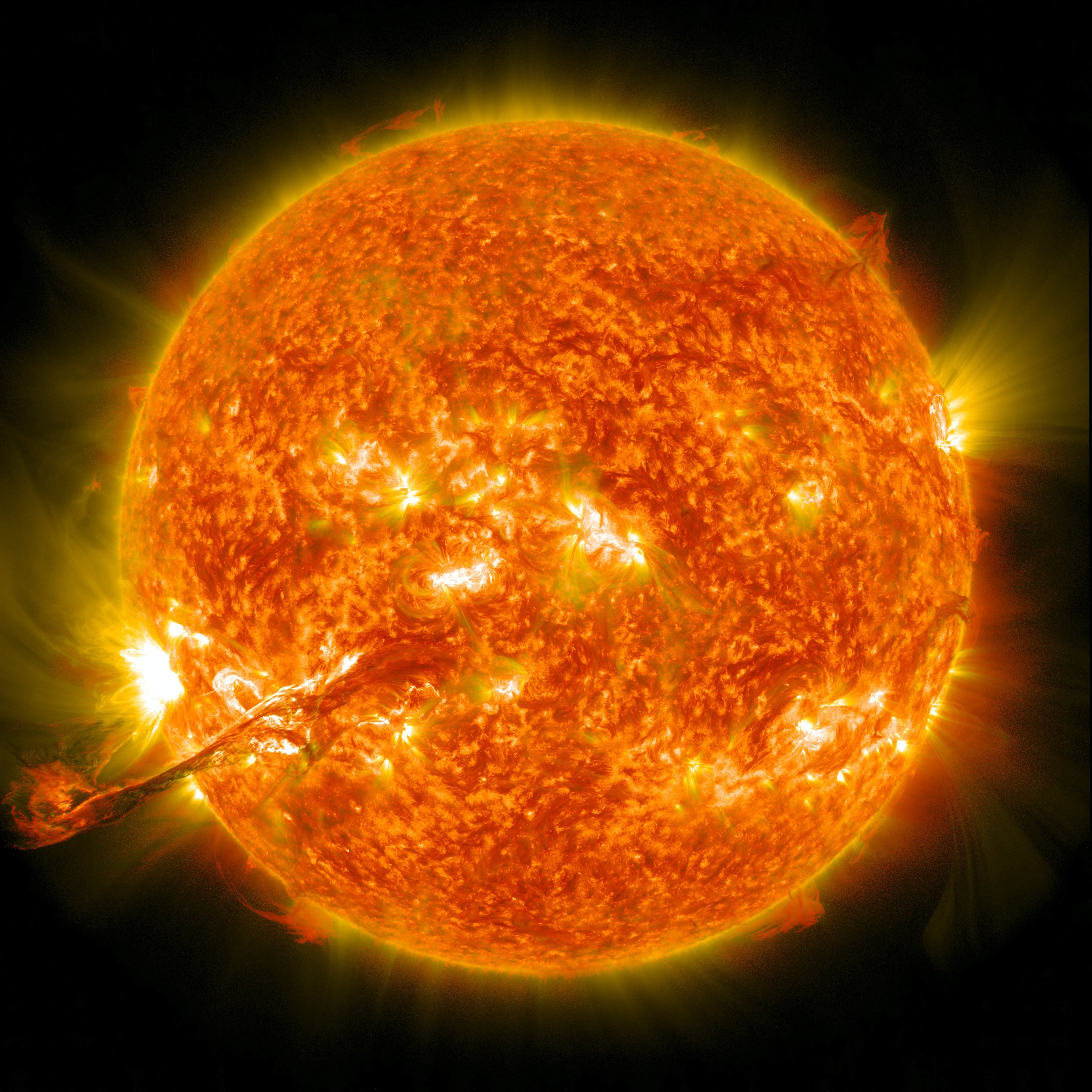

Photo by NASA on Unsplash
The more 'spots' on the Sun's surface, the higher the Sun's output
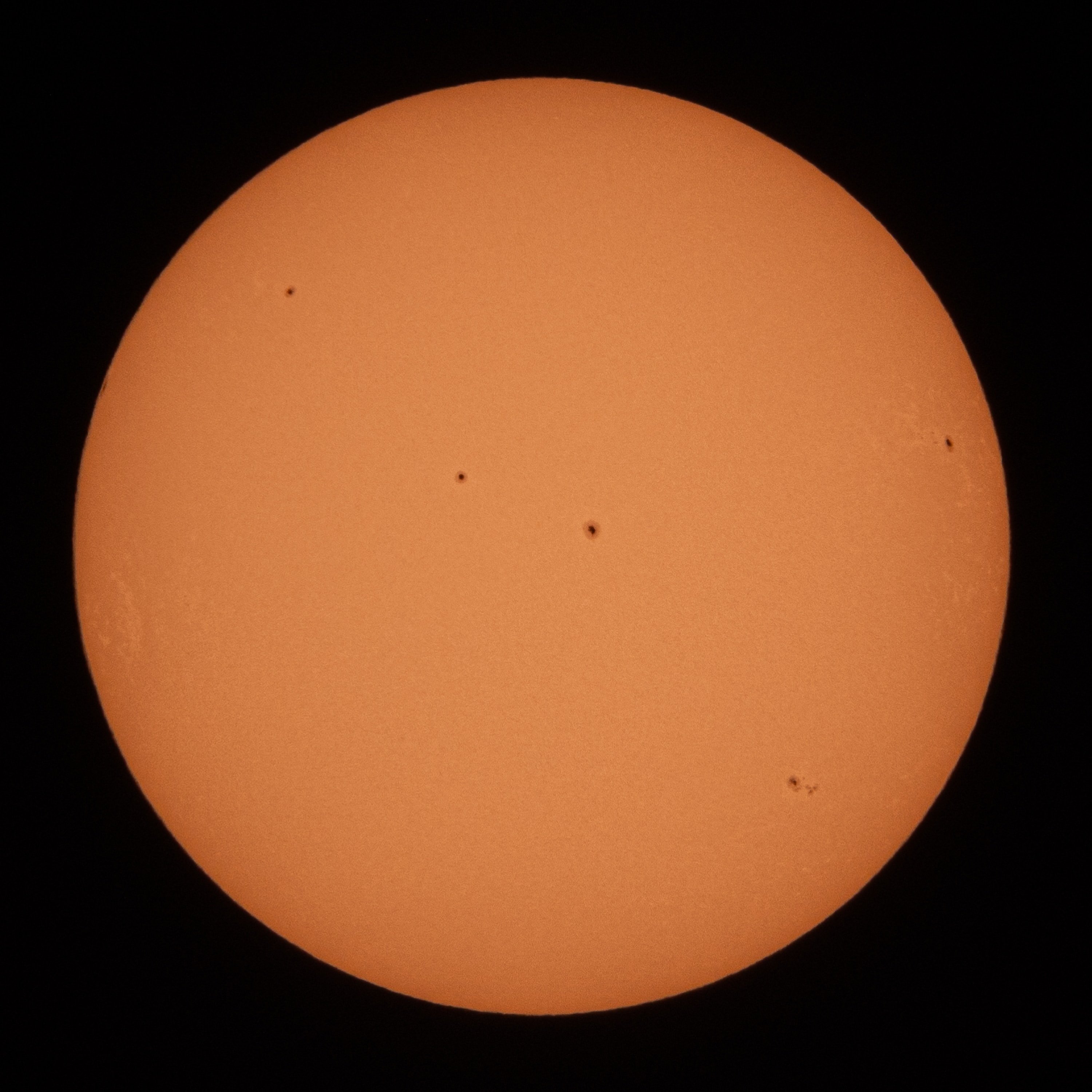

Photo by The Adaptive on Unsplash
Evidence of natural climate change
The evidence for the natural changes comes from a range of sources
Ice cores
These trap ash, air bubbles, and microbes
The air bubbles contain CO2, providing information about past temperatures
Ice cores give information regarding the climate for the last 2.6 million years
Handling an ice-core

Ice-cores are drilled and stored in large freezers, ready to be examined
Preserved pollen
Sediment cores taken from peat bogs and lake beds may contain preserved pollen
Looking under a microscope, it is possible to identify which plant it came from
Scientists then work out which climatic conditions were needed for the plant to grow and where they grew
Pollen under a microscope

Pollen viewed under a microscope shows the types of flowers that grew in the past
Historical sources
Historical paintings, books, newspapers and diaries provide evidence of what the climate used to be like
Records of agricultural reports show what crop yields were like
The Met Office has collected weather conditions going back as far as 1861
Photographic records show how glaciers have retreated
Paintings such as the frost fairs on the Thames in London in the 19th Century
Diaries kept by people such as a gentleman farmer from North-West England dating back to 1815
Books by authors such as Charles Dickens and Sir Arthur Conan Doyle
These are subjective and so may be inaccurate

The frost fair in full swing. Photo: Wikicommons
Tree rings
Fossilized tree remains enable scientists to examine the climate over thousands of years
The study of tree rings is called dendrochronology
Each year, a new tree ring is formed
During good growing conditions, such as warmer and wetter years, trees grow more and so the rings are thicker
If the rings are narrow and close together, there is less growth, indicating a cooler period
Tree growth

Tree rings can show past climate conditions
Worked Example
Choose the correct definition of climate change
(1 mark)
A: Global warming
B: Large-scale, long-term changes in average temperatures and weather patterns
C: The difference in temperature and weather during different seasons
D: The short-term warming of the Earth
Answer:
B: Large-scale, long-term changes in average temperature and weather patterns (1)
The alternatives are incorrect because:
A: Global warming is the rise in temperatures due to increased levels of greenhouse gases
C: The changes in temperature and weather are short-term
D: Short-term warming does not affect long-term weather patterns

You've read 0 of your 0 free revision notes
Get unlimited access
to absolutely everything:
- Downloadable PDFs
- Unlimited Revision Notes
- Topic Questions
- Past Papers
- Model Answers
- Videos (Maths and Science)
Did this page help you?