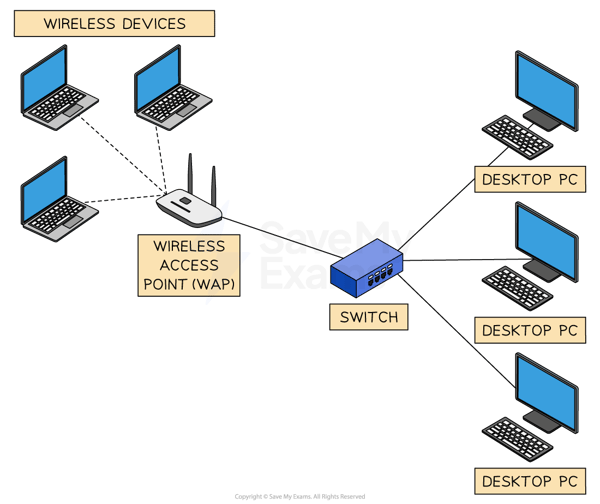
(a) State one wireless method used to connect devices on a Personal Area Network (PAN) [1]
(b) A travel agent has offices in two sites that are 10 miles apart. Describe two differences between a Local Area Network (LAN) and a Wide Area Network (WAN) [2]
Answers
- (a) Bluetooth
- (b) Max two marks from
-
- LANs cover relatively small geographical areas // WANs usually cover a wide geographic area
- LANs often owned and controlled/managed by a single person/organisation // WANs often under collective/distributed ownership
- WANs are (usually) several LANs connected together
- WANs (usually) have a much larger number of devices/users than LANs
- LAN has a lower latency // WAN has higher latency
- WANs are (usually) slower than LANs
- The cost-per-byte for transmission is much higher on a WAN
- LANs and WANs use different protocols