Types of Cell Division
Mitosis
The function of mitosis
- Mitosis is a nuclear division that gives rise to two genetically identical, diploid daughter cells
- Human diploid cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes
- All body cells are produced by mitosis
- Note that this does not apply to gametes
- Mitosis is required for:
- Growth: mitosis produces new cells and allows organisms to increase in size
- Replacement: old cells are replaced with new cells when they die
- Repair: damaged tissues can be repaired
- Asexual reproduction: in some organisms, mitosis produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent
The outcome of mitosis
- Before mitosis begins the chromosomes replicate, resulting in X-shaped chromosomes with two 'arms' known as chromatids
- During mitosis, the following events occur:
- The chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell
- The chromatids are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell
- A new nucleus forms around each new group of chromosomes
- Mitosis results in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells
- The daughter cells have the same chromosome number as the parent cell
Mitosis diagram

Mitosis produces two genetically identical daughter cells
Meiosis
The function of meiosis
- Cells in reproductive organs divide by meiosis to form gametes
- Gametes include sperm cells and egg cells in animals, and pollen grains and ovules in plants
- Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction
- Meiosis halves the chromosome number, producing haploid daughter cells
- If this were not the case then fertilisation would double the number of chromosomes
- Meiosis halves the chromosome number, producing haploid daughter cells
- Meiosis increases genetic variation in offspring
- Meiosis recombines maternal and paternal chromosomes in different ways, ensuring that gametes are genetically different to each other and to the parent cell
The outcome of meiosis
- Before meiosis begins each chromosome is replicated
- During meiosis, there are two divisions:
- First division: the pairs of chromosomes line up along the centre of the cell and are pulled apart so that each new cell only contains one member of each pair
- Second division: the chromosomes line up along the centre of the cell and the arms of the chromosomes are pulled apart
- Meiosis produces four genetically different daughter cells
- The cells contain half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell
Meiosis diagram

Meiosis produces four genetically different daughter cells
Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis
Comparison of mitosis and meiosis table
| Feature | Mitosis | Meiosis |
| Rounds of cell division | One | Two |
| Number of daughter cells | Two | Four |
| Chromosomes number in daughter cells | Diploid | Haploid |
| Daughter cells are genetically... | ...identical | ...different |
| Location | Normal body cells | Reproductive organs |
| Cell type produced | Body cells | Gametes |
| Role | Growth, replacement and repair | Sexual reproduction |
Comparison of mitosis and meiosis diagram
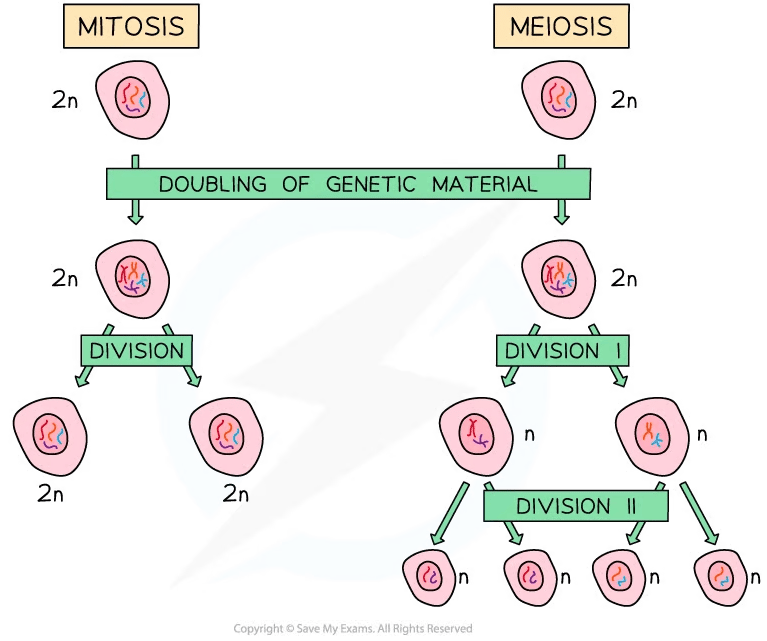
Mitosis produces 2 diploid daughter cells while meiosis produces 4 haploid daughter cells
Exam Tip
Make sure that you are happy with the spelling of mitosis and meiosis; getting the spelling wrong here may mean that examiners don't know which of the two terms you intended to use.

