2.45B Practical: The Effect of Light on Gas Exchange in Plants (Edexcel IGCSE Biology)
Revision Note

Author
LáraExpertise
Biology Lead
Practical: The Effect of Light on Gas Exchange in Plants
Apparatus
- Boiling tubes
- Cotton wool
- Aluminium foil
- Gauze
- Rubber bungs
- Hydrogencarbonate indicator
- Leaves
Method
- Measure out 20 cm3 hydrogencarbonate indicator into 4 boiling tubes
- Put some cotton wool into each boiling tube
- Label the boiling tubes A-D and set them up as follows:
- Tube A - No leaf (control tube)
- Tube B - Place a leaf in the tube and leave in the light
- Tube C - Place a leaf in the tube and wrap it in aluminium foil to block out the light
- Tube D - Place a leaf in the tube and wrap it in gauze to allow partial light
- Put a bung into the top of each tube
- Leave all 4 tubes in the light for 30 minutes

Hydrogencarbonate indicator can be used to study gas exchange in different light conditions
Results
- After 30 minutes, we would expect the following results:
- Tube A - The control tube should remain an orange/red colour to show that the carbon dioxide is at atmospheric levels
- There has been no net movement
- Tube B - This tube was placed in the light with a leaf which is photosynthesizing and respiring
- Because the rate of photosynthesis is greater than the rate of respiration, the hydrogencarbonate indicator will turn purple as there is less carbon dioxide than atmospheric levels
- Tube C - This tube had a leaf inside, but was wrapped in aluminium foil meaning that no sunlight could reach the leaf
- No light means that this leaf will not photosynthesize but will still be respiring and therefore producing carbon dioxide. The indicator will turn yellow as carbon dioxide levels increase above atmospheric levels
- Tube D - This tube had a leaf inside and was wrapped in gauze allowing partial light
- This means that the rate of photosynthesis equals the rate of respiration so there was no net change in carbon dioxide levels and the indicator remained orange/red

Hydrogencarbonate indicator will change from orange/red to yellow with increasing carbon dioxide or purple with decreasing carbon dioxide
The Effect of Light on Net Gas Exchange in Plants Table

Applying CORMS evaluation to practical work
- When working with practical investigations, remember to consider your CORMS evaluation
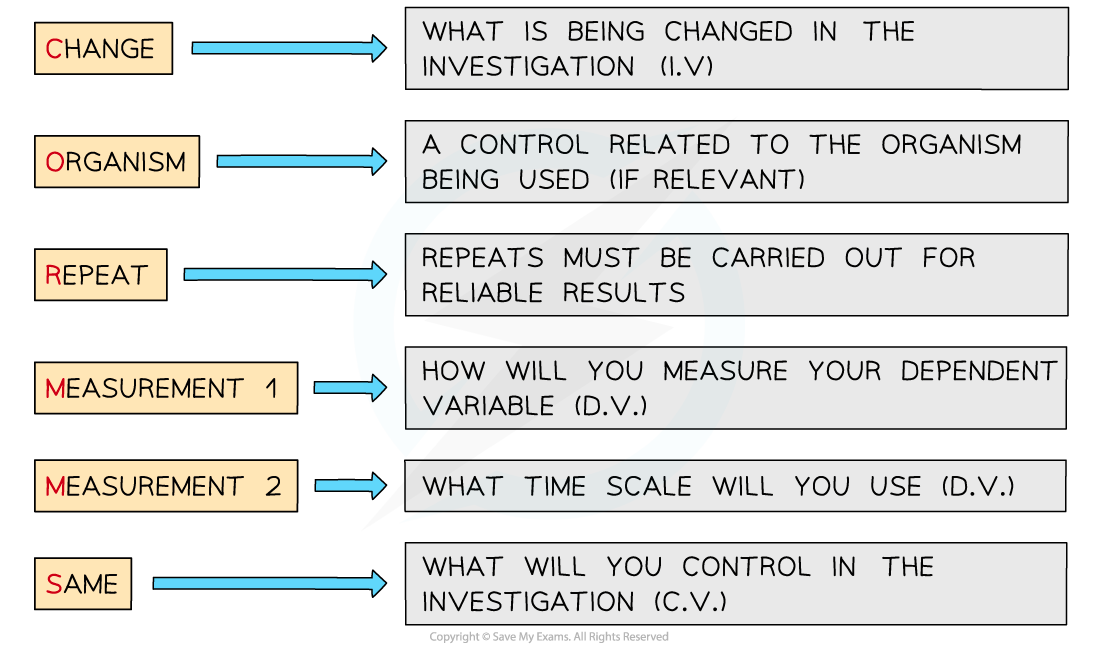
CORMS evaluation
- In this investigation, your evaluation should look something like this:
- Change - We will change the availability of light for each boiling tube (not wrapped, wrapped in foil, wrapped in gauze)
- Organisms - The leaves should be from the same species/age of the plant, they should be approximately the same size
- Repeat - We will repeat the investigation several times to ensure our results are reliable
- Measurement 1 - We will observe the change in the hydrogen carbonate indicator
- Measurement 2 - after 30 minutes
- Same - We will control the volume of hydrogen carbonate indicator, the number of leaves, the temperature of the environment

You've read 0 of your 0 free revision notes
Get unlimited access
to absolutely everything:
- Downloadable PDFs
- Unlimited Revision Notes
- Topic Questions
- Past Papers
- Model Answers
- Videos (Maths and Science)
Did this page help you?