Constructing PGFs
What are Probability Generating Functions (PGFs)?
- A probability generating function,
, is a polynomial in
- The powers of
are the values of
- The coefficients are the corresponding probabilities of
- The powers of
- For example:
-
0 1 4 5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 - The PGF is
This simplifies to
-
- The variable
is called a dummy variable
- It is used to create a polynomial structure
- Do not confuse it with
- Coefficients can never be negative
- They are probabilities!
What is the value of G(1)?
always
- This is because substituting
into a PGF:
- Turns all powers of
into 1
- Leaves the sum of all probabilities which equals 1
- For example
- Turns all powers of
What is E(tX)?
is the formal definition of a PGF given in the Formulae Booklet
- Recall that
is the expectation of
- Th expectation of a function of
is
- Th expectation of a function of
- Choosing the function to be
gives
- This is the sum of powers of
multiplied by their corresponding probabilities
- That is the probability generating function of
- This is the sum of powers of
- Recall that
Exam Tip
- Don't forget to use
in harder algebraic questions!
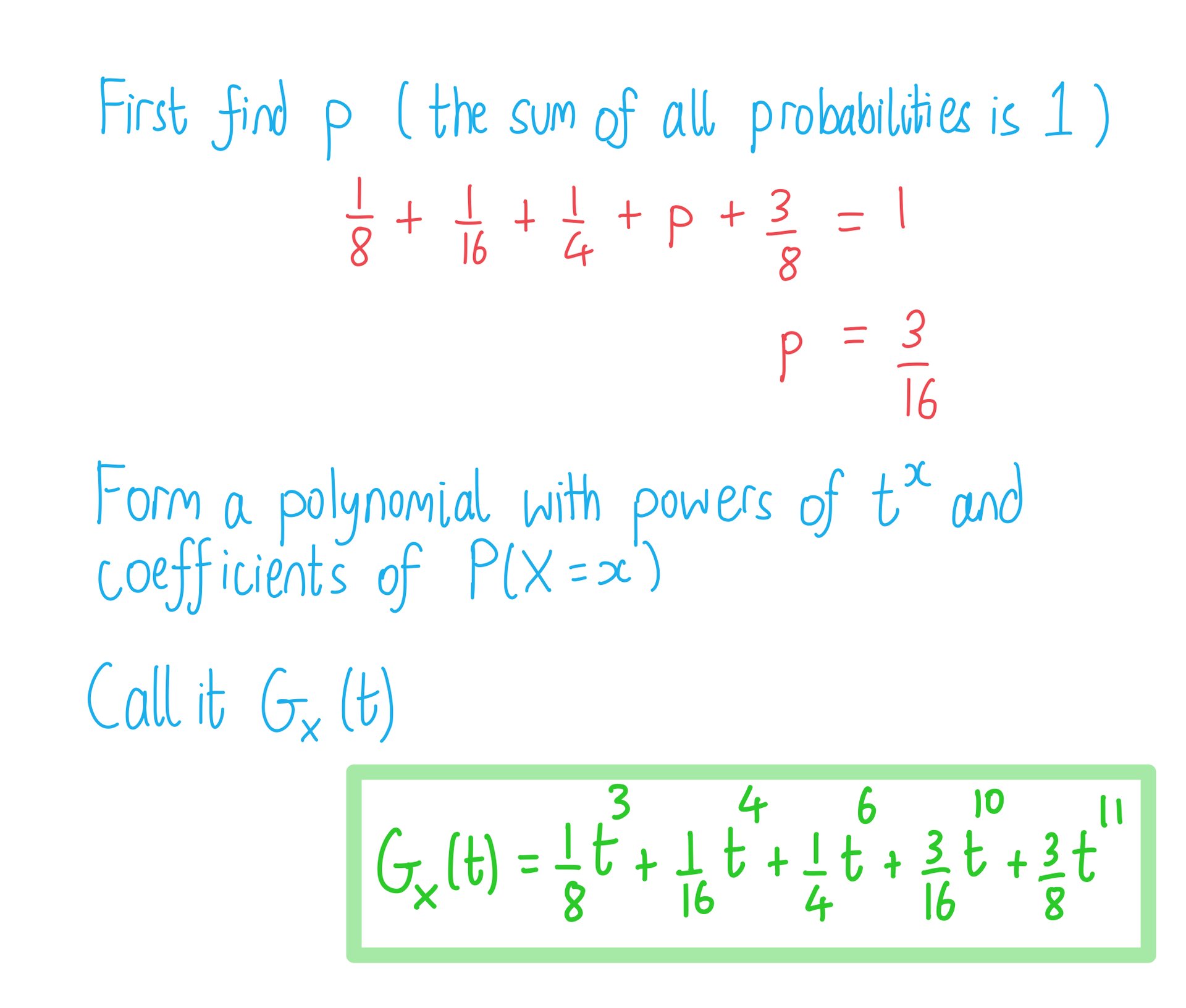
Worked example
A discrete random variable, , is given by the probability distribution below.
| 3 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 11 | |
Find the probability generating function of .