PGFs of Standard Distributions
What are the PGFs of standard distributions?
- You are given the following PGFs in the Formulae Booklet:
-
Distribution of P.G.F. Binomial Poisson Geometric on 1, 2, ...
Negative binomial on ,
, ...
-
How do I find the PGF of a Binomial Distribution?
- If
then
where
- You can use this to to prove, by differentiation, that
- You can use this to to prove, by differentiation, that
- To derive the PGF, create a probability distribution table
- Using the binomial probability function
- From
to
- Showing all powers clearly
-
0 1 2 ... ...
- Using the binomial probability function
- Write down the PGF as a polynomial
- Group the
and
together in brackets
- Spot that this is the binomial expansion of
- Since
- So
- Since
- The proof can also be done in summation (sigma) notation
How do I find the PGF of a Poisson Distribution?
- If
then
- You can use this to to prove, by differentiation, that
- You can use this to to prove, by differentiation, that
- To derive the PGF, create a probability distribution table
- Using the Poisson probability function
- From
x to infinity
- Showing all powers clearly
-
0 1 2 3 ... ...
- Using the Poisson probability function
- Write down the PGF as a polynomial
- Group the
and
together in brackets
- Factorise out
- Spot that the Maclaurin series of
is inside the brackets
- Since
- So
- Since
- Add the powers then factorise out
- The proof can also be done in summation (sigma) notation
How do I find the PGF of a Geometric Distribution?
- If
then
where
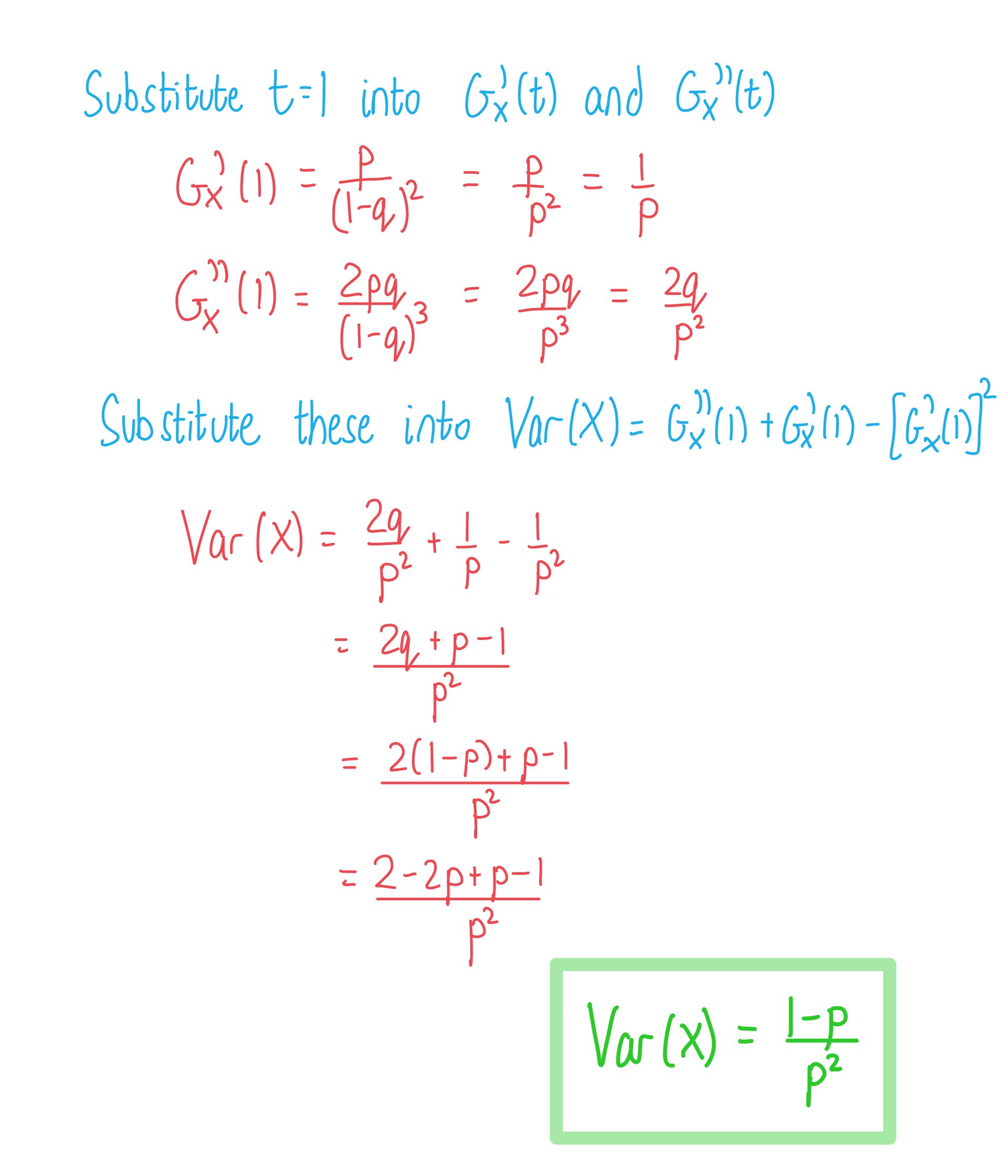
- You can use this to to prove, by differentiation, that
- You can use this to to prove, by differentiation, that
- To derive the PGF, create a probability distribution table
- Using the Geometric probability function
- From
to infinity (
)
- Simplify the powers
-
1 2 3 4 ... ...
- Using the Geometric probability function
- Write down the PGF as a polynomial
- Spot that this is an infinite geometric series with first term
and common ratio
- Use
- So
- Use
How do I find the PGF of a Negative Binomial Distribution?
- If
then
where
- You can use this to to prove, by differentiation, that
- You can use this to to prove, by differentiation, that
- To derive the PGF, the proof is best done in summation (sigma) notation
- Use the negative binomial probability function
- From
to infinity
- From
- Use the negative binomial probability function
- To proceed, you will be given in the question the result that
- Write
as
to group
and
together in brackets
- Factorise
out (as it does not depend on
)
- Use the result given, where
- Write as one bracket to the power
- Write
Exam Tip
- The words derive or from first principles mean you have to prove the PGF (not quote it)
Worked example
Write down the probability generating function for the distribution and use it to prove that
.