Electrolysis Experiments (Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry)
Revision Note

Author
StewartExpertise
Chemistry Lead
Electrolysis of Molten Compounds
- Lead(II) bromide is a binary ionic compound meaning that it is a compound consisting of just two elements joined together by ionic bonding
- When these compounds are heated beyond their melting point, they become molten and can conduct electricity as their ions can move freely and carry the charge
- These compounds undergo electrolysis and always produce their corresponding element
- To predict the products of any binary molten compound first identify the ions present
- The positive ion will migrate towards the cathode and the negative ion will migrate towards the anode
- Therefore the cathode product will always be the metal and the product formed at the anode will always be the non-metal

Diagram showing the electrolysis of lead(II) bromide
Method:
- Add lead(II) bromide into a crucible and heat so it will turn molten, allowing ions to be free to move and conduct an electric charge
- Add two graphite rods as the electrodes and connect this to a power pack or battery
- Turn on the power pack or battery and allow electrolysis to take place
- Negative bromide ions move to the positive electrode (anode) and lose two electrons to form bromine molecules. There is bubbling at the anode as brown bromine gas is given off
- Positive lead ions move to the negative electrode (cathode) and gain electrons to form grey lead metal which deposits on the bottom of the electrode
Exam Tip
Remember electrodes need to be inert such as graphite or platinum so that they don’t participate in a side reaction with the electrolyte.
Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions
Rules:
- Aqueous solutions will always have water present
- Some water molecules split up into hydrogen and hydroxide ions, H+ and OH–, which participate in the electrolysis reactions
Positive Electrode
- OH– ions and non-metal ions are attracted to the positive electrode
- Either OH– or non-metal ions will lose electrons and oxygen gas or a non-metal is released e.g. chlorine
- The product formed depends on which ion loses electrons more readily
Negative Electrode
- H+ ions and metal ions are attracted to the negative electrode but only one will gain electrons
- Either hydrogen or a metal will be produced
- If the metal is above hydrogen in reactivity series, hydrogen will be produced – bubbling will be seen at the cathode
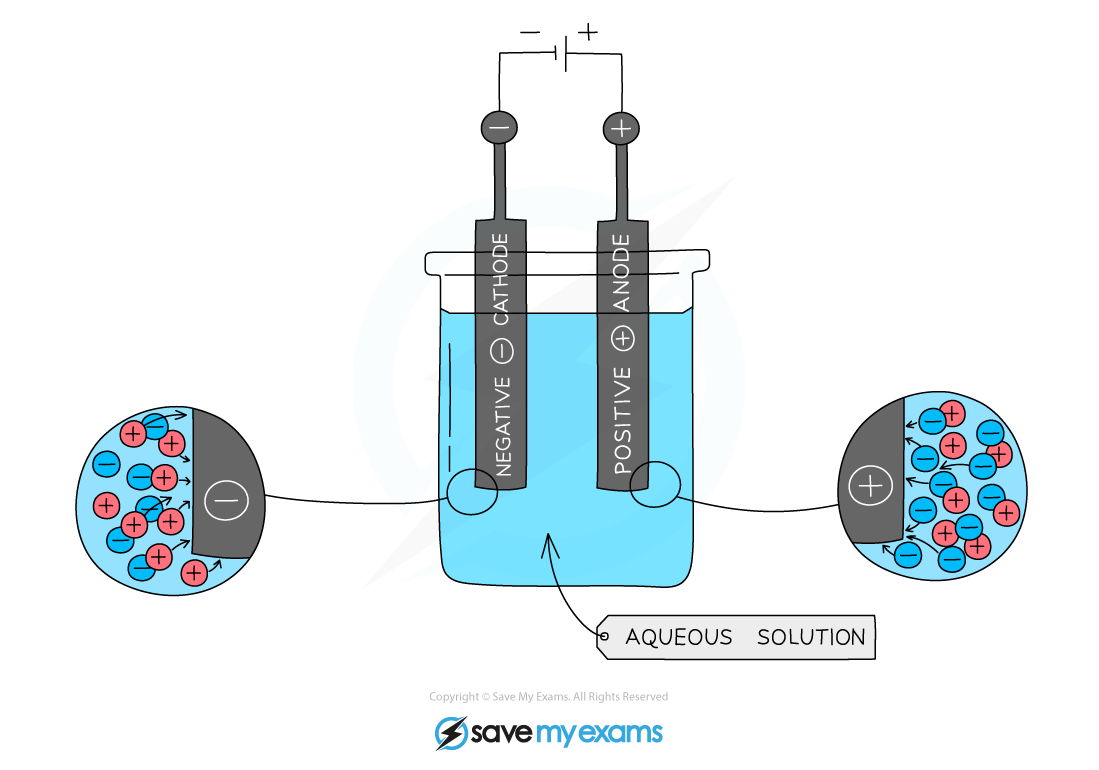
The electrolysis of aqueous solutions
- The apparatus can be modified for the collection of gases by using inverted test tubes over the electrodes
- The electrodes are made from graphite which is inert and does not interfere with the electrolysis reactions
Exam Tip
Once you have identified the ions, the next step is to decide towards which electrode will they be drawn and identify the product formed. It helps if you recall the reactivity series.

You've read 0 of your 0 free revision notes
Get unlimited access
to absolutely everything:
- Downloadable PDFs
- Unlimited Revision Notes
- Topic Questions
- Past Papers
- Model Answers
- Videos (Maths and Science)
Did this page help you?