Orbital Period (Edexcel IGCSE Physics)
Revision Note

Author
AshikaExpertise
Physics Project Lead
Calculating Orbital Period
- When planets move around the Sun, or a moon moves around a planet, they orbit in circular motion
- This means that in one orbit, a planet travels a distance equal to the circumference of a circle (the shape of the orbit)
- This is equal to 2πr where r is the radius a circle
- The relationship between speed, distance and time is:
- the average orbital speed of an object can be defined by the equation:
- Where:
- v = orbital speed in metres per second (m/s)
- r = average radius of the orbit in metres (m)
- T = orbital period in seconds (s)
- This orbital period (or time period) is defined as:
The time taken for an object to complete one orbit
- The orbital radius r is always taken from the centre of the object being orbited to the object orbiting

Orbital radius and orbital speed of a planet moving around a Sun
Worked example
The Hubble Space Telescope moves in a circular orbit. Its distance above the Earth’s surface is 560 km and the radius of the Earth is 6400 km. It completes one orbit in 96 minutes.
Calculate its orbital speed in m/s.
Step 1: List the known quantities
-
- Radius of the Earth = 6400 km
- Distance of the telescope above the Earth's surface = 560 km
- Time period, T = 96 minutes
Step 2: Write the relevant equation
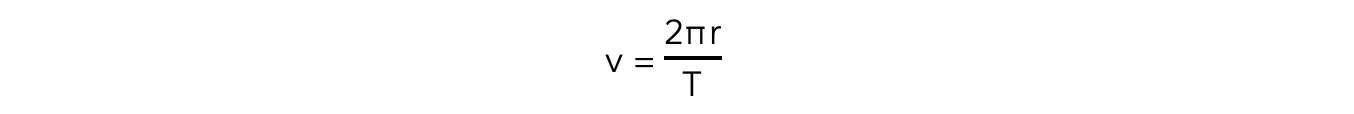
Step 3: Calculate the orbital radius, r
-
- The orbital radius is the distance from the centre of the Earth to the telescope
r = Radius of the Earth + Distance of the telescope above the Earth's surface
r = 6400 + 560 = 6960 km
Step 4: Convert any units
-
- The time period needs to be in seconds
1 minute = 60 seconds
96 minutes = 60 × 96 = 5760 s
-
- The radius needs to be in metres
1 km = 1000 m
6960 km = 6 960 000 m
Step 5: Substitute values into the orbital speed equation

Exam Tip
Remember to always check that the orbital period r given is the distance from the centre of the Sun (if a planet is orbiting a Sun) or the planet (if a moon is orbiting a planet) and not just from the surface

You've read 0 of your 0 free revision notes
Get unlimited access
to absolutely everything:
- Downloadable PDFs
- Unlimited Revision Notes
- Topic Questions
- Past Papers
- Model Answers
- Videos (Maths and Science)
Did this page help you?