Snell's Law (Edexcel IGCSE Physics)
Revision Note

Author
Katie MExpertise
Physics
Snell's Law
- When light enters a denser medium (such as glass) it slows down and bends towards the normal
- How much the light bends depends on the density of the material

Angle of incidence i and angle of refraction r through a glass block
- If light travels from a less dense to a more dense medium (e.g. air to glass), r < i (bends towards the normal)
- If light travels from a more dense to a less dense medium (e.g. glass to air), r > i (bends away from the normal)
- The angles of incidence and refraction are related by an equation known as Snell's Law:

- Where:
- n = the refractive index of the material
- i = angle of incidence of the light (°)
- r = angle of refraction of the light (°)
- 'Sin' is the trigonometric function 'sine' which is on a scientific calculator
- This equation can be rearranged with the help of the formula triangle:
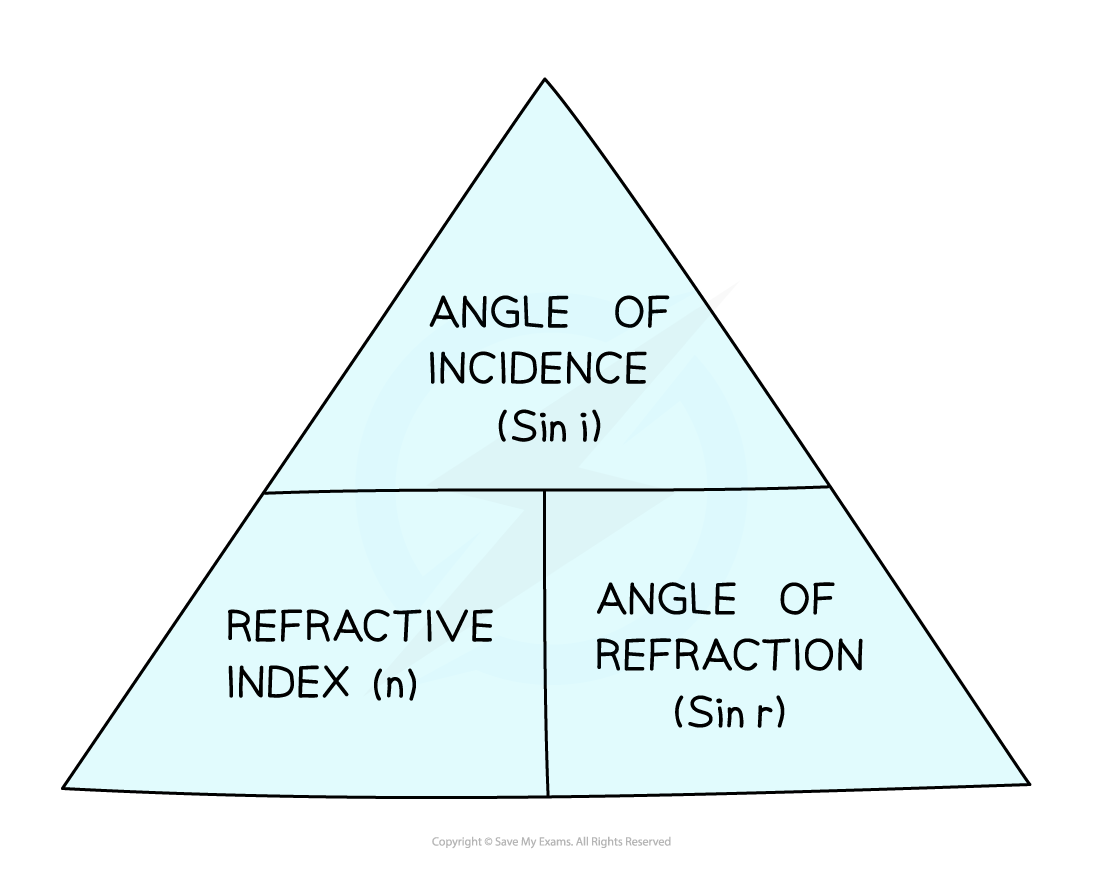
Snell's law formula triangle
- The refractive index is a number which is related to the speed of light in the material (which is always less than the speed of light in a vacuum):

- The refractive index is a number that is always larger than 1 and is different for different materials
- Objects which are more optically dense have a higher refractive index, eg. n is about 2.4 for diamond
- Objects which are less optically dense have a lower refractive index, eg. n is about 1.5 for glass
- Since refractive index is a ratio, it has no units
Worked example
A ray of light enters a glass block of refractive index 1.53 making an angle of 15° with the normal before entering the block.Calculate the angle it makes with the normal after it enters the glass block.
Step 1: List the known quantities
- Refractive index of glass, n = 1.53
- Angle of incidence, i = 15°
Step 2: Write the equation for Snell's Law
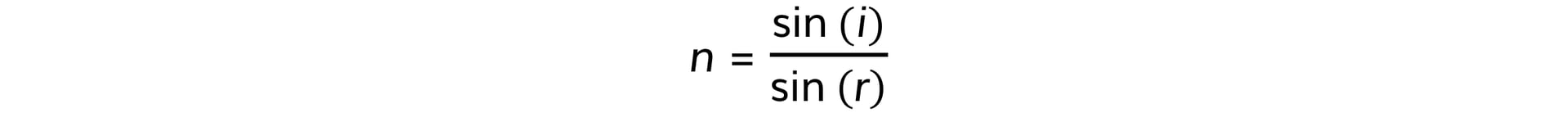
Step 3: Rearrange the equation and calculate sin (r)

Step 4: Find the angle of refraction (r) by using the inverse sin function
r = sin–1 (0.1692) = 9.7 = 10°
Exam Tip
Important: (sin i / sin r) is not the same as (i / r). Incorrectly cancelling the sin terms is a very common mistake!When calculating the value of i or r start by calculating the value of sin i or sin r.You can then use the inverse sin function (sin–1 on most calculators by pressing 'shift' then 'sine') to find the angle.One way to remember which way around i and r are in the fraction is remembering that 'i' comes before 'r' in the alphabet, and therefore is on the top of the fraction (whilst r is on the bottom).

You've read 0 of your 0 free revision notes
Get unlimited access
to absolutely everything:
- Downloadable PDFs
- Unlimited Revision Notes
- Topic Questions
- Past Papers
- Model Answers
- Videos (Maths and Science)
Did this page help you?