Sexual Reproduction in Plants (CIE IGCSE Biology)
Revision Note

Author
PhilExpertise
Biology Project Lead
Insect-Pollinated Flowers
- Flowers are the reproductive organ of the plant
- They usually contain both male and female reproductive parts
- Plants produce pollen which contains a nucleus inside that is the male gamete
- Unlike the male gamete in humans (sperm), pollen is not capable of locomotion (moving from one place to another)
- This means plants have to have mechanisms in place to transfer pollen from the anther to the stigma
- This process is known as pollination and there are two main mechanisms by which it occurs: transferred by insects (or other animals like birds) or transferred by wind
- The structure of insect and wind-pollinated flowers are slightly different as each is adapted for their specific function
Parts of the flower

General flower structure
 Structure of a flower
Structure of a flower
Features of an insect-pollinated flower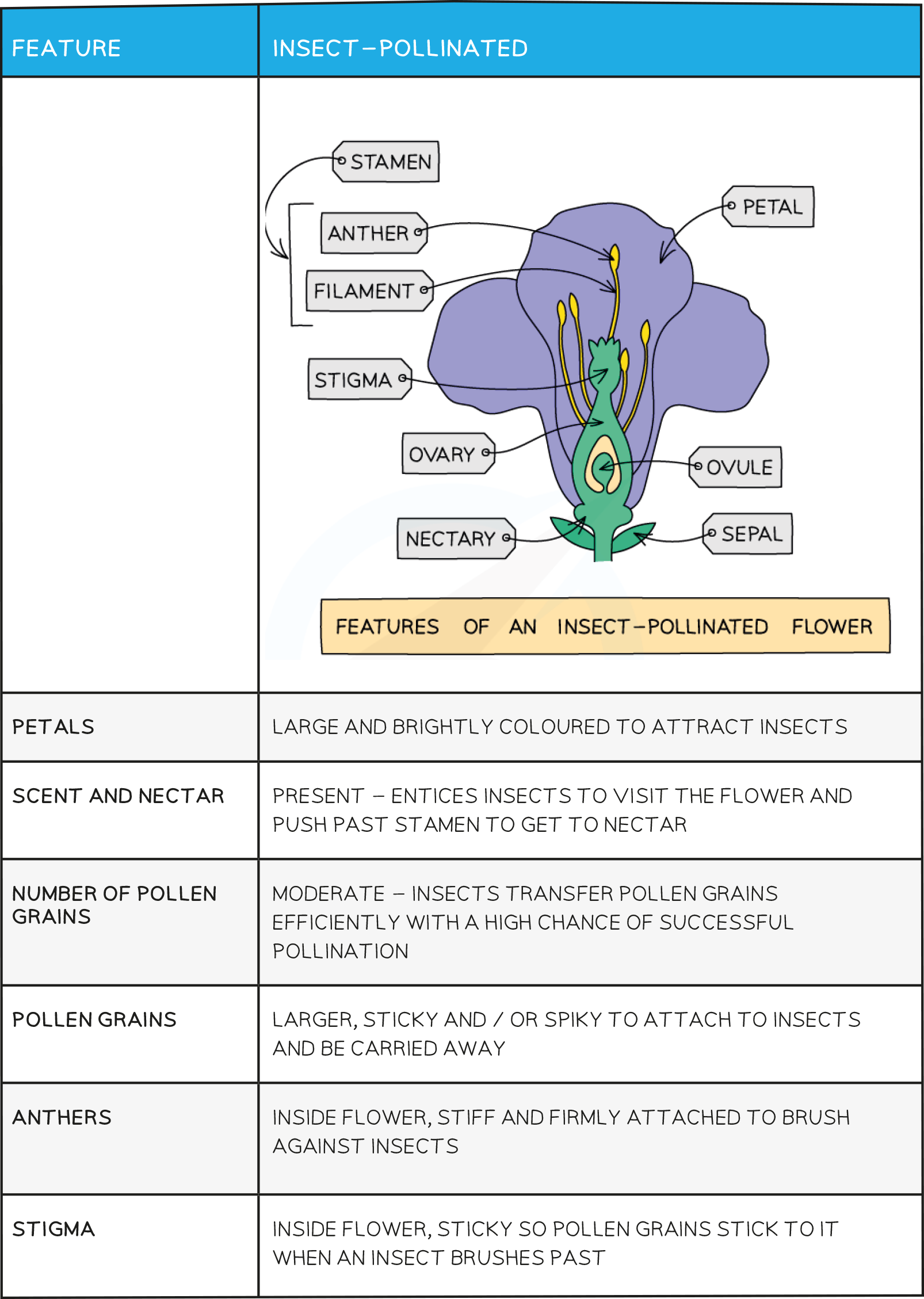
Wind-Pollinated Flowers
Features of a wind-pollinated flower
- The pollen produced by insect and wind-pollinated flowers is also different:
- Insect pollinated flowers produce smaller amounts of larger, heavier pollen grains that often contain spikes or hooks on the outside so they are better able to stick to insects
- Wind pollinated flowers produce large amounts of small, lightweight pollen grains that are usually smooth
Here is an example of a multiple-choice question asking students to use their knowledge to identify types of pollen grain:
 A multiple-choice question asking students to use their knowledge to identify types of pollen grain
A multiple-choice question asking students to use their knowledge to identify types of pollen grain
Pollination & Fertilisation
Pollination
- Pollination is discussed above as the ways in which pollen grains can be transferred from an anther to a stigma
Fertilisation
- Fertilisation occurs when a pollen nucleus fuses with an ovum nucleus in the ovule
- As the pollen has no ‘tail’ to swim to the ovary of a plant, in order to reach the ‘female’ nucleus in the ovary it has to grow a pollen tube
- This only happens if the pollen grain has landed on the right kind of stigma (i.e. of the same species as the flower the pollen came from)
- The nucleus inside the pollen grain slips down the tube as it grows down the style towards the ovary
- The ovary contains one or more ovules which each contain an ovum with a female nucleus that a male pollen nucleus can fuse with
- Once the nuclei (pl) have joined together, that ovule has been fertilised and a zygote has been formed
- The zygote will start to divide and eventually form a seed within the ovule
- As different plants have different numbers of ovules, this explains why different fruits (which develop from the ovary) have different numbers of seeds (which develop from the ovules)
 Growth of a pollen tube
Growth of a pollen tube
 Fertilisation in a flowering plant
Fertilisation in a flowering plant
Exam Tip
Students often get confused between pollination and fertilisation in plants, but they are not the same thing.
Think of pollination as the plant’s equivalent to human sexual intercourse – after sex, the male sex cells (sperm) have been deposited into the female. But, for fertilisation to occur, the nucleus from a male sperm cell has to fuse with the nucleus of a female sex cell (egg) and the sperm has to travel to find the egg before this happens. It’s exactly the same in plants!
Factors Affecting Germination of Seeds
- Germination is the start of growth in the seed
- Three factors are required for successful germination:
- Water - allows the seed to swell up and the enzymes in the embryo to start working so that growth can occur
- Oxygen - so that energy can be released for germination
- Warmth - germination improves as temperature rises (up to a maximum) as the reactions which take place are controlled by enzymes
- As carbon dioxide is not necessary for germination but also does not inhibit it, it makes no difference whether it is present or not
Investigating Germination
- Set up 4 boiling tubes each containing 10 cress seeds on cotton wool
- Set each test tube as shown in diagram below
- Leave tubes in set environment for a period of time: A, B and C incubated at 20°C; D placed in a fridge at 4°C
- Compare results and see which tube has the greatest number of germinated seeds
 Conditions required for germination
Conditions required for germination
Conditions required for germination - results:
Self- & Cross-Pollination: Extended
Self- & Cross-Pollination: Extended
- Cross-pollination occurs when the pollen from one plant is transferred to the stigma of another plant of the same species
- This is the way most plants carry out pollination as it improves genetic variation
- Occasionally, the pollen from a flower can land on its own stigma or on the stigma of another flower on the same plant - this is known as self-pollination
- Self-pollination reduces genetic variety of the offspring as all the gametes come from the same parent (and are therefore genetically identical)
- Lack of variation in the offspring is a disadvantage if environmental conditions change, as it is less likely that any offspring will have adaptations that suit the new conditions well
- On the other hand, cross-pollination relies completely on the presence of pollinators and this can be a problem if those pollinators are missing (eg the reduction in bee numbers is of great importance to humans as bees pollinate a large number of food crops) - this doesn’t apply to wind-pollinated plants


Growth of the pollen tube and its entry into the ovule followed by fertilisation

You've read 0 of your 0 free revision notes
Get unlimited access
to absolutely everything:
- Downloadable PDFs
- Unlimited Revision Notes
- Topic Questions
- Past Papers
- Model Answers
- Videos (Maths and Science)
Did this page help you?