Exact Trig Values (OCR GCSE Maths)
Revision Note

Author
AmberExpertise
Maths
Exact Trig Values
What are exact values in trigonometry?
- For certain angles the values of sin θ, cos θ and tan θ can be written exactly
- This means using fractions and surds
- You should be familiar with these values and be able to derive the values using geometry
- You are expected to know the exact values of sin, cos and tan for angles of 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°, 180° and their multiples
- The exact values you are expected to know are summarised here:

- Note that the values of sin θ going from 0° to 90° match those of cos θ going from 90° to 0°
How are exact values in trigonometry derived?
- There are two special right-angled triangles that can be used to derive all of the exact values you need to know
- Consider a right-angles triangle with a hypotenuse of 2 units and a shorter side length of 1 unit
- Using Pythagoras’ theorem the third side will be
- The angles will be 90°, 60° and 30°
- Using SOHCAHTOA gives…
- Sin 60° =
Sin 30° =
- Cos 60° =
Cos 30° =
- Tan 60° =
Tan 30° =
=
- Sin 60° =
- Using Pythagoras’ theorem the third side will be
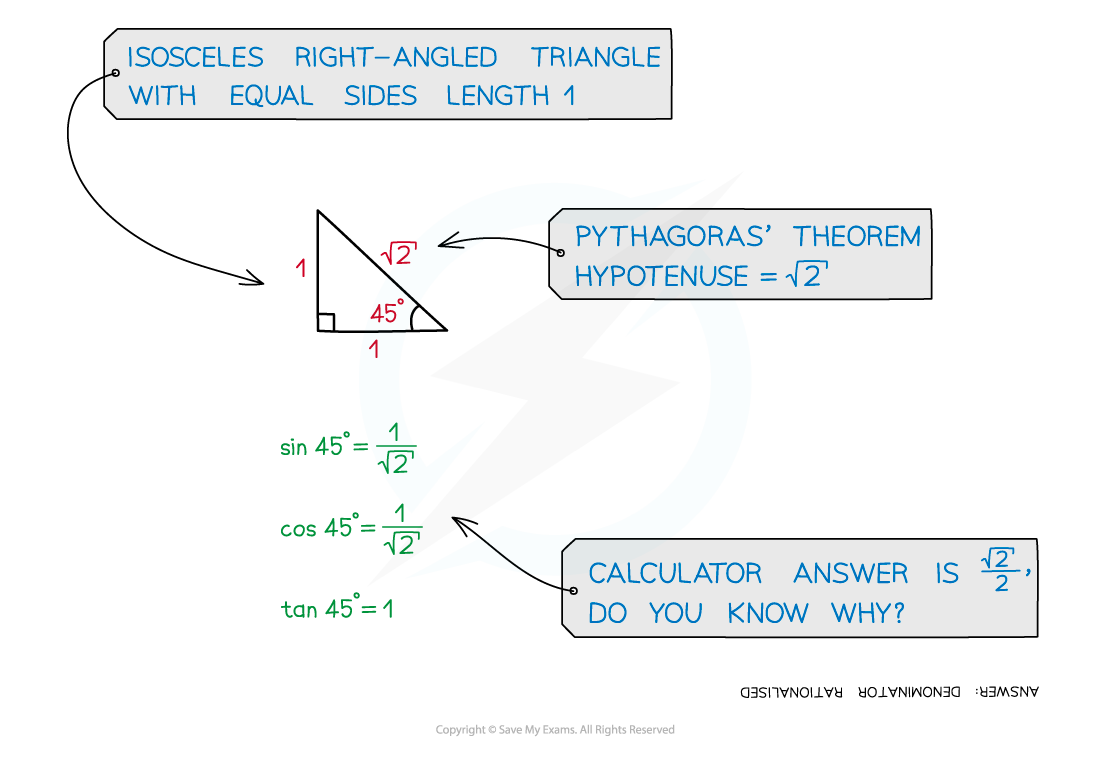
- Consider an isosceles triangle with two equal side lengths (the opposite and adjacent) of 1 unit
- Using Pythagoras’ theorem it will have a hypotenuse of
- The two equal angles will be 45°
- Using SOHCAHTOA gives…
- Sin
- Cos
- Tan
= 1
- Sin
- Using Pythagoras’ theorem it will have a hypotenuse of
Exam Tip
- You will be expected to be comfortable using exact trig values for certain angles but it can be easy to muddle them up if you just try to remember them from a list
- sketch the triangles and trig graphs on your paper so that you can use them as many times as you need to during the exam
- sketch the triangles for the key angles
,
,
- sketch the trig graphs for the key angles
,
,
,
,
- sketch the triangles for the key angles
Worked example
Using an equilateral triangle of side length 2 units, derive the exact values for the sine, cosine and tangent of 60° and 30°.
Sketch the triangle and create two right angled triangles by drawing the line of symmetry through the middle.

Use Pythagoras' theorem to find the vertical height of the triangle.
Use SOHCAHTOA to find the trig ratios for 30° and 60°.
Sin 60° = Sin 30° =
Cos 60° = Cos 30° =
Tan 60° = Tan 30° =
=

You've read 0 of your 0 free revision notes
Get unlimited access
to absolutely everything:
- Downloadable PDFs
- Unlimited Revision Notes
- Topic Questions
- Past Papers
- Model Answers
- Videos (Maths and Science)
Did this page help you?