Amplitude & Intensity
Intensity
- The intensity of a wave is defined as follows:
Power per unit area
- Intensity is measured in W m–2
- Power is defined as:
The rate of energy transfer
- Therefore, intensity can also be defined as:
The rate of energy transfer per unit area
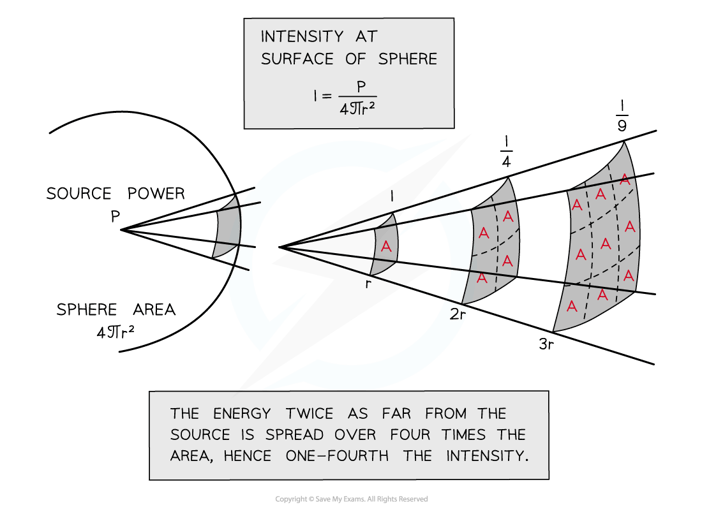
- For spherical waves being emitted by a point source equally in all directions, the intensity follows an inverse square law with distance from the point source
- Where:
- I = intensity of the wave in watts per metre squared (W m–2)
- r = distance from the point source in metres (m)
- For spherical waves being emitted by a point source equally in all directions, the intensity at the surface of a sphere is calculated using:
I =
- Where:
- P = power in watts (W)
- r = radius of sphere in metres (m)
- For spherical waves being emitted by a point source equally in all directions, the power is a constant, therefore the relationship can be expressed as:
I ∝
- This is an example of an inverse square law relationship
I ∝ x−2
Intensity decreases by the inverse square law
Intensity Variation with Amplitude
- By definition, the intensity of a wave (its power per unit area) is proportional to the energy transferred by the wave
- The intensity of a wave at a particular point is related to the amplitude of the wave at that point
- The energy transferred by a wave is proportional to the square of the amplitude
- Therefore, the intensity of a wave is proportional to the square of the amplitude
- Where:
- I = intensity of the wave in W m–2
- A = amplitude of the wave in metres (m)
Worked example
A person stands 10 m away from a loudspeaker. The sound produced by the loudspeaker is very loud, so the person moves 20 m away from it.
State the effect of this change on the intensity and the amplitude of the sound waves heard by the person.
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
-
- Original distance, r1 = 10 m
- New distance, r2 = 20 m
Step 2: Write down the relationship between the intensity of a wave and the distance from the point source producing the wave
![]()
Step 2: State the new intensity
-
- Since the distance doubles (r2 = 2r1), the intensity is reduced by a factor four
![]()
Step 3: Write down the relationship between the intensity of a wave and its amplitude
![]()
Step 4: State the new amplitude
-
- Since the intensity is reduced by a factor four, the amplitude decreases by half
![]()

