5.2.2 Techniques of Differentiation
Chain Rule
What is the chain rule?
- The chain rule states if
is a function of
and
is a function of
then
-
- This is given in the formula booklet
- In function notation this could be written
How do I know when to use the chain rule?
- The chain rule is used when we are trying to differentiate composite functions
- “function of a function”
- these can be identified as the variable (usually
) does not ‘appear alone’
– not a composite function,
‘appears alone’
is a composite function;
is tripled and has 2 added to it before the sine function is applied
How do I use the chain rule?
STEP 1
Identify the two functions
Rewrite  as a function of
as a function of ;
; %3C%2Fmo%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'math17f39f8317fbdb1988ef4c628eb'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAADRjdnQgDVUNBwAAAVAAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGMAAAAsmhlYWQQC2qxAAACQAAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAAngAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAAKcAAAACGxvY2EAHTwYAAACpAAAAAxtYXhwBT0FPgAAArAAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAALQAAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAEcAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABJAAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACAAAAAEAAQAAQAAAD3%2F%2FwAAAD3%2F%2F%2F%2FEAAEAAAAAAAABVAMsAIABAABWACoCWAIeAQ4BLAIsAFoBgAKAAKAA1ACAAAAAAAAAACsAVQCAAKsA1QEAASsABwAAAAIAVQAAAwADqwADAAcAADMRIRElIREhVQKr%2FasCAP4AA6v8VVUDAAACAIAA6wLVAhUAAwAHAGUYAbAIELAG1LAGELAF1LAIELAB1LABELAA1LAGELAHPLAFELAEPLABELACPLAAELADPACwCBCwBtSwBhCwB9SwBxCwAdSwARCwAtSwBhCwBTywBxCwBDywARCwADywAhCwAzwxMBMhNSEdASE1gAJV%2FasCVQHAVdVVVQAAAAEAAAABAADVeM5BXw889QADBAD%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F1joTc%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FWOhNzAAD%2FIASAA6sAAAAKAAIAAQAAAAAAAQAAA%2Bj%2FagAAF3AAAP%2B2BIAAAQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAIDUgBVA1YAgAAAAAAAAAAoAAAAsgABAAAAAgBeAAUAAAAAAAIAgAQAAAAAAAQAAN4AAAAAAAAAFQECAAAAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAAAAAAAAAIADgASAAAAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAAAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAAAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAAAAAAAAAYACQB4AAAAAAAAAAgAHACBAAEAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAEAAAAAAAIADgASAAEAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAEAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAEAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAEAAAAAAAYACQB4AAEAAAAAAAgAHACBAAMAAQQJAAEAEgAAAAMAAQQJAAIADgASAAMAAQQJAAMAMAAgAAMAAQQJAAQAEgBQAAMAAQQJAAUAFgBiAAMAAQQJAAYACQB4AAMAAQQJAAgAHACBAE0AYQB0AGgAIABGAG8AbgB0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQAVgBlAHIAcwBpAG8AbgAgADEALgAwTWF0aF9Gb250AE0AYQB0AGgAcwAgAEYAbwByACAATQBvAHIAZQAAAwAAAAAAAAH0APoAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAALkHEQAAjYUYALIAAAAVFBOxAAE%2F)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%228.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ey%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math17f39f8317fbdb1988ef4c628eb%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2222.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2234.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ef%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2243.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2250.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Eu%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2258.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E)
Write  as a function of
as a function of ;
; %3C%2Fmo%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'math17f39f8317fbdb1988ef4c628eb'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAADRjdnQgDVUNBwAAAVAAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGMAAAAsmhlYWQQC2qxAAACQAAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAAngAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAAKcAAAACGxvY2EAHTwYAAACpAAAAAxtYXhwBT0FPgAAArAAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAALQAAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAEcAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABJAAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACAAAAAEAAQAAQAAAD3%2F%2FwAAAD3%2F%2F%2F%2FEAAEAAAAAAAABVAMsAIABAABWACoCWAIeAQ4BLAIsAFoBgAKAAKAA1ACAAAAAAAAAACsAVQCAAKsA1QEAASsABwAAAAIAVQAAAwADqwADAAcAADMRIRElIREhVQKr%2FasCAP4AA6v8VVUDAAACAIAA6wLVAhUAAwAHAGUYAbAIELAG1LAGELAF1LAIELAB1LABELAA1LAGELAHPLAFELAEPLABELACPLAAELADPACwCBCwBtSwBhCwB9SwBxCwAdSwARCwAtSwBhCwBTywBxCwBDywARCwADywAhCwAzwxMBMhNSEdASE1gAJV%2FasCVQHAVdVVVQAAAAEAAAABAADVeM5BXw889QADBAD%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F1joTc%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FWOhNzAAD%2FIASAA6sAAAAKAAIAAQAAAAAAAQAAA%2Bj%2FagAAF3AAAP%2B2BIAAAQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAIDUgBVA1YAgAAAAAAAAAAoAAAAsgABAAAAAgBeAAUAAAAAAAIAgAQAAAAAAAQAAN4AAAAAAAAAFQECAAAAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAAAAAAAAAIADgASAAAAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAAAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAAAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAAAAAAAAAYACQB4AAAAAAAAAAgAHACBAAEAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAEAAAAAAAIADgASAAEAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAEAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAEAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAEAAAAAAAYACQB4AAEAAAAAAAgAHACBAAMAAQQJAAEAEgAAAAMAAQQJAAIADgASAAMAAQQJAAMAMAAgAAMAAQQJAAQAEgBQAAMAAQQJAAUAFgBiAAMAAQQJAAYACQB4AAMAAQQJAAgAHACBAE0AYQB0AGgAIABGAG8AbgB0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQAVgBlAHIAcwBpAG8AbgAgADEALgAwTWF0aF9Gb250AE0AYQB0AGgAcwAgAEYAbwByACAATQBvAHIAZQAAAwAAAAAAAAH0APoAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAALkHEQAAjYUYALIAAAAVFBOxAAE%2F)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%228.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Eu%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math17f39f8317fbdb1988ef4c628eb%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2222.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2235.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Eg%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2244.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2251.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2259.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E)
STEP 2
Differentiate  with respect to
with respect to  to get
to get
Differentiate  with respect to
with respect to  to get
to get
STEP 3
Obtain  by applying the formula
by applying the formulaformat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%226.5%22%20x2%3D%2228.5%22%20y1%3D%2223.5%22%20y2%3D%2223.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2212.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2221.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ey%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2212.5%22%20y%3D%2241%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2221.5%22%20y%3D%2241%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math102a87acd26f5771b4d57a7dfb3%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2239.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%2250.5%22%20x2%3D%2272.5%22%20y1%3D%2223.5%22%20y2%3D%2223.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2256.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2265.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ey%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2256.5%22%20y%3D%2241%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2265.5%22%20y%3D%2241%22%3Eu%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math102a87acd26f5771b4d57a7dfb3%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2283.5%22%20y%3D%2230%22%3E%26%23xD7%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%2294.5%22%20x2%3D%22116.5%22%20y1%3D%2223.5%22%20y2%3D%2223.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22100.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22109.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Eu%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22100.5%22%20y%3D%2241%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22109.5%22%20y%3D%2241%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) and substitute
and substitute back in for
back in for%3C%2Fmo%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%228.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Eg%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2217.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2224.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2232.5%22%20y%3D%2216%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E)
-
In trickier problems chain rule may have to be applied more than once
Are there any standard results for using chain rule?
- There are five general results that can be useful
- If
then
- If
-
- If
then
- If
then
- If
then
- If
then
- If
Exam Tip
- You should aim to be able to spot and carry out the chain rule mentally (rather than use substitution)
- every time you use it, say it to yourself in your head
“differentiate the first function ignoring the second, then multiply by the derivative of the second function"
- every time you use it, say it to yourself in your head
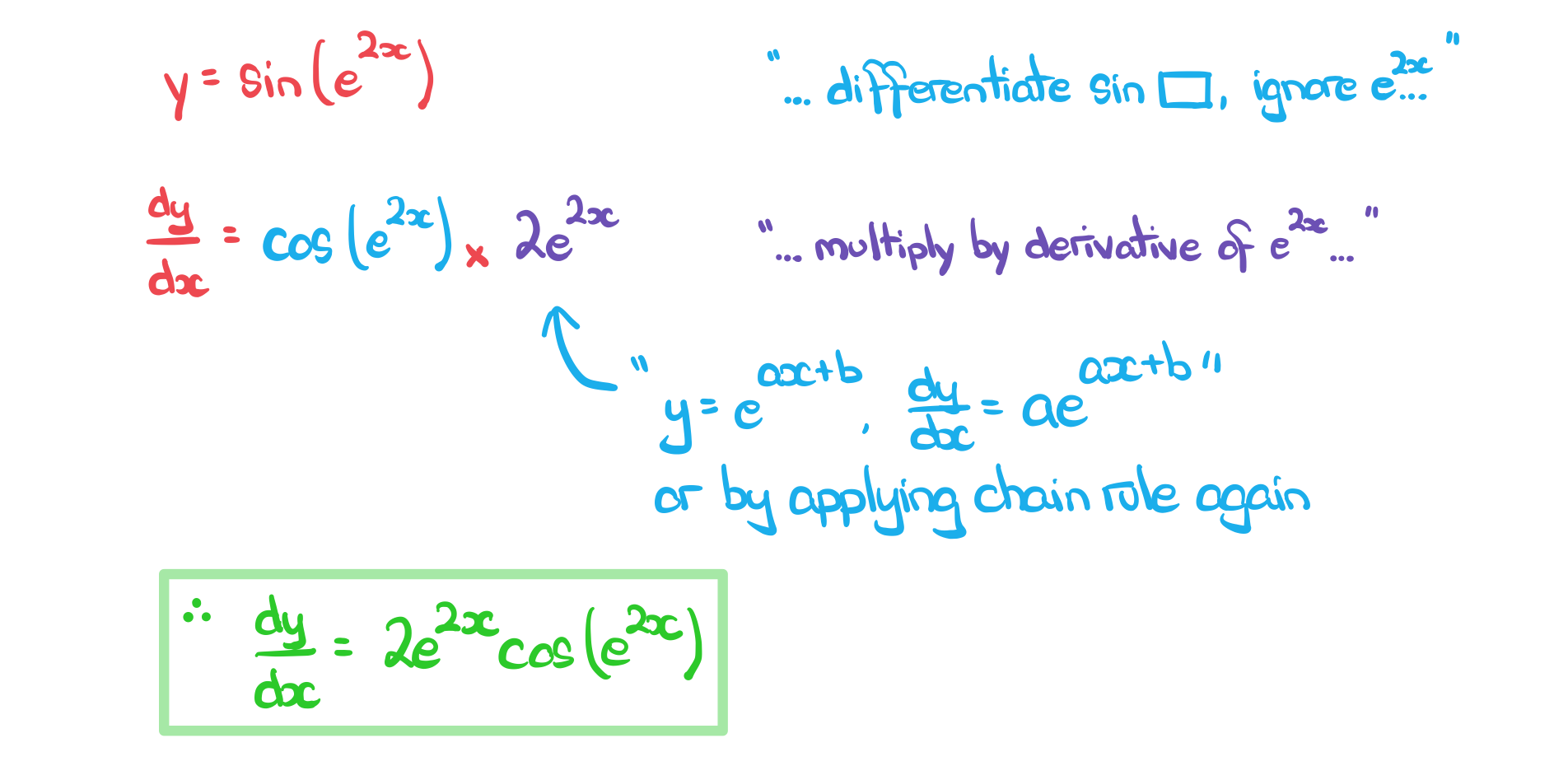
Worked example
a)
Find the derivative of%3C%2Fmo%3E%3C%2Fmrow%3E%3Cmn%3E7%3C%2Fmn%3E%3C%2Fmsup%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'math190bc3972c7934354efb2af01e7'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAAERjdnQgDVUNBwAAAWAAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGcAAABdWhlYWQQC2qxAAADFAAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAA0wAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAANwAAAAEGxvY2EAHTwYAAADgAAAABRtYXhwBT0FPgAAA5QAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAAO0AAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAFVAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABXQAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEADAAAAAIAAgAAgAAACsAPSIS%2F%2F8AAAArAD0iEv%2F%2F%2F9b%2Fxd3xAAEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAVQDLACAAQAAVgAqAlgCHgEOASwCLABaAYACgACgANQAgAAAAAAAAAArAFUAgACrANUBAAErAAcAAAACAFUAAAMAA6sAAwAHAAAzESERJSERIVUCq%2F2rAgD%2BAAOr%2FFVVAwAAAQCAAFUC1QKrAAsASQEYsgwBARQTELEAA%2FaxAQT1sAo8sQMF9bAIPLEFBPWwBjyxDQPmALEAABMQsQEG5LEBARMQsAU8sQME5bELBfWwBzyxCQTlMTATIREzESEVIREjESGAAQBVAQD%2FAFX%2FAAGrAQD%2FAFb%2FAAEAAAIAgADrAtUCFQADAAcAZRgBsAgQsAbUsAYQsAXUsAgQsAHUsAEQsADUsAYQsAc8sAUQsAQ8sAEQsAI8sAAQsAM8ALAIELAG1LAGELAH1LAHELAB1LABELAC1LAGELAFPLAHELAEPLABELAAPLACELADPDEwEyE1IR0BITWAAlX9qwJVAcBV1VVVAAEAgAFVAtUBqwADADAYAbAEELEAA%2FawAzyxAgf1sAE8sQUD5gCxAAATELEABuWxAAETELABPLEDBfWwAjwTIRUhgAJV%2FasBq1YAAAAAAQAAAAEAANV4zkFfDzz1AAMEAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FWOhNz%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Y6E3MAAP8gBIADqwAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAD6P9qAAAXcAAA%2F7YEgAABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABANSAFUDVgCAA1YAgANWAIAAAAAAAAAAKAAAAKEAAAErAAABdQABAAAABABeAAUAAAAAAAIAgAQAAAAAAAQAAN4AAAAAAAAAFQECAAAAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAAAAAAAAAIADgASAAAAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAAAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAAAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAAAAAAAAAYACQB4AAAAAAAAAAgAHACBAAEAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAEAAAAAAAIADgASAAEAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAEAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAEAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAEAAAAAAAYACQB4AAEAAAAAAAgAHACBAAMAAQQJAAEAEgAAAAMAAQQJAAIADgASAAMAAQQJAAMAMAAgAAMAAQQJAAQAEgBQAAMAAQQJAAUAFgBiAAMAAQQJAAYACQB4AAMAAQQJAAgAHACBAE0AYQB0AGgAIABGAG8AbgB0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQAVgBlAHIAcwBpAG8AbgAgADEALgAwTWF0aF9Gb250AE0AYQB0AGgAcwAgAEYAbwByACAATQBvAHIAZQAAAwAAAAAAAAH0APoAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAALkHEQAAjYUYALIAAAAVFBOxAAE%2F)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%228.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3Ey%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math190bc3972c7934354efb2af01e7%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2222.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2234.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2241.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2213%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2250.5%22%20y%3D%2212%22%3E2%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math190bc3972c7934354efb2af01e7%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2262.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3E%26%23x2212%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2275.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3E5%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2284.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math190bc3972c7934354efb2af01e7%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2298.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3E%2B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22111.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3E7%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22118.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2213%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22125.5%22%20y%3D%2212%22%3E7%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) .
.

b)
Find the derivative of%3C%2Fmo%3E%3C%2Fmath%3E--%3E%3Cdefs%3E%3Cstyle%20type%3D%22text%2Fcss%22%3E%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'math17f39f8317fbdb1988ef4c628eb'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMi7iBBMAAADMAAAATmNtYXDEvmKUAAABHAAAADRjdnQgDVUNBwAAAVAAAAA6Z2x5ZoPi2VsAAAGMAAAAsmhlYWQQC2qxAAACQAAAADZoaGVhCGsXSAAAAngAAAAkaG10eE2rRkcAAAKcAAAACGxvY2EAHTwYAAACpAAAAAxtYXhwBT0FPgAAArAAAAAgbmFtZaBxlY4AAALQAAABn3Bvc3QB9wD6AAAEcAAAACBwcmVwa1uragAABJAAAAAUAAADSwGQAAUAAAQABAAAAAAABAAEAAAAAAAAAQEAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAg1UADev96AAAD6ACWAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACAAAAAEAAQAAQAAAD3%2F%2FwAAAD3%2F%2F%2F%2FEAAEAAAAAAAABVAMsAIABAABWACoCWAIeAQ4BLAIsAFoBgAKAAKAA1ACAAAAAAAAAACsAVQCAAKsA1QEAASsABwAAAAIAVQAAAwADqwADAAcAADMRIRElIREhVQKr%2FasCAP4AA6v8VVUDAAACAIAA6wLVAhUAAwAHAGUYAbAIELAG1LAGELAF1LAIELAB1LABELAA1LAGELAHPLAFELAEPLABELACPLAAELADPACwCBCwBtSwBhCwB9SwBxCwAdSwARCwAtSwBhCwBTywBxCwBDywARCwADywAhCwAzwxMBMhNSEdASE1gAJV%2FasCVQHAVdVVVQAAAAEAAAABAADVeM5BXw889QADBAD%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F1joTc%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FWOhNzAAD%2FIASAA6sAAAAKAAIAAQAAAAAAAQAAA%2Bj%2FagAAF3AAAP%2B2BIAAAQAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAIDUgBVA1YAgAAAAAAAAAAoAAAAsgABAAAAAgBeAAUAAAAAAAIAgAQAAAAAAAQAAN4AAAAAAAAAFQECAAAAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAAAAAAAAAIADgASAAAAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAAAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAAAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAAAAAAAAAYACQB4AAAAAAAAAAgAHACBAAEAAAAAAAEAEgAAAAEAAAAAAAIADgASAAEAAAAAAAMAMAAgAAEAAAAAAAQAEgBQAAEAAAAAAAUAFgBiAAEAAAAAAAYACQB4AAEAAAAAAAgAHACBAAMAAQQJAAEAEgAAAAMAAQQJAAIADgASAAMAAQQJAAMAMAAgAAMAAQQJAAQAEgBQAAMAAQQJAAUAFgBiAAMAAQQJAAYACQB4AAMAAQQJAAgAHACBAE0AYQB0AGgAIABGAG8AbgB0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQATQBhAHQAaAAgAEYAbwBuAHQAVgBlAHIAcwBpAG8AbgAgADEALgAwTWF0aF9Gb250AE0AYQB0AGgAcwAgAEYAbwByACAATQBvAHIAZQAAAwAAAAAAAAH0APoAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAALkHEQAAjYUYALIAAAAVFBOxAAE%2F)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%40font-face%7Bfont-family%3A'round_brackets18549f92a457f2409'%3Bsrc%3Aurl(data%3Afont%2Ftruetype%3Bcharset%3Dutf-8%3Bbase64%2CAAEAAAAMAIAAAwBAT1MvMjwHLFQAAADMAAAATmNtYXDf7xCrAAABHAAAADxjdnQgBAkDLgAAAVgAAAASZ2x5ZmAOz2cAAAFsAAABJGhlYWQOKih8AAACkAAAADZoaGVhCvgVwgAAAsgAAAAkaG10eCA6AAIAAALsAAAADGxvY2EAAARLAAAC%2BAAAABBtYXhwBIgEWQAAAwgAAAAgbmFtZXHR30MAAAMoAAACOXBvc3QDogHPAAAFZAAAACBwcmVwupWEAAAABYQAAAAHAAAGcgGQAAUAAAgACAAAAAAACAAIAAAAAAAAAQIAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAACAgICAAAAAo8AMGe%2F57AAAHPgGyAAAAAAACAAEAAQAAABQAAwABAAAAFAAEACgAAAAGAAQAAQACACgAKf%2F%2FAAAAKAAp%2F%2F%2F%2F2f%2FZAAEAAAAAAAAAAAFUAFYBAAAsAKgDgAAyAAcAAAACAAAAKgDVA1UAAwAHAAA1MxEjEyMRM9XVq4CAKgMr%2FQAC1QABAAD%2B0AIgBtAACQBNGAGwChCwA9SwAxCwAtSwChCwBdSwBRCwANSwAxCwBzywAhCwCDwAsAoQsAPUsAMQsAfUsAoQsAXUsAoQsADUsAMQsAI8sAcQsAg8MTAREAEzABEQASMAAZCQ%2FnABkJD%2BcALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAA%2FtACIAbQAAkATRgBsAoQsAPUsAMQsALUsAoQsAXUsAUQsADUsAMQsAc8sAIQsAg8ALAKELAD1LADELAH1LAKELAF1LAKELAA1LADELACPLAHELAIPDEwARABIwAREAEzAAIg%2FnCQAZD%2BcJABkALQ%2FZD%2BcAGQAnACcAGQ%2FnAAAQAAAAEAAPW2NYFfDzz1AAMIAP%2F%2F%2F%2F%2FVre7u%2F%2F%2F%2F%2F9Wt7u4AAP7QA7cG0AAAAAoAAgABAAAAAAABAAAHPv5OAAAXcAAA%2F%2F4DtwABAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAwDVAAACIAAAAiAAAAAAAAAAAAAkAAAAowAAASQAAQAAAAMACgACAAAAAAACAIAEAAAAAAAEAABNAAAAAAAAABUBAgAAAAAAAAABAD4AAAAAAAAAAAACAA4APgAAAAAAAAADAFwATAAAAAAAAAAEAD4AqAAAAAAAAAAFABYA5gAAAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAAAAAAAAAAIABwBGwABAAAAAAABAD4AAAABAAAAAAACAA4APgABAAAAAAADAFwATAABAAAAAAAEAD4AqAABAAAAAAAFABYA5gABAAAAAAAGAB8A%2FAABAAAAAAAIABwBGwADAAEECQABAD4AAAADAAEECQACAA4APgADAAEECQADAFwATAADAAEECQAEAD4AqAADAAEECQAFABYA5gADAAEECQAGAB8A%2FAADAAEECQAIABwBGwBSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFIAZQBnAHUAbABhAHIATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlACAAUgBvAHUAbgBkACAAYgByAGEAYwBrAGUAdABzACAAdwBpAHQAaAAgAGEAcwBjAGUAbgB0ACAAMQA4ADUANABSAG8AdQBuAGQAIABiAHIAYQBjAGsAZQB0AHMAIAB3AGkAdABoACAAYQBzAGMAZQBuAHQAIAAxADgANQA0AFYAZQByAHMAaQBvAG4AIAAyAC4AMFJvdW5kX2JyYWNrZXRzX3dpdGhfYXNjZW50XzE4NTQATQBhAHQAaABzACAARgBvAHIAIABNAG8AcgBlAAAAAAMAAAAAAAADnwHPAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAC5B%2F8AAY2FAA%3D%3D)format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%228.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3Ey%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math17f39f8317fbdb1988ef4c628eb%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2222.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2241.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3Esin%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2255.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3E(%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2262.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3Ee%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2213%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2269.5%22%20y%3D%2212%22%3E2%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2213%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2276.5%22%20y%3D%2212%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22round_brackets18549f92a457f2409%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2283.5%22%20y%3D%2217%22%3E)%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) .
.
Product Rule
What is the product rule?
- The product rule states if
is the product of two functions
and
then
-
- This is given in the formula booklet
- In function notation this could be written as
- ‘Dash notation’ may be used as a shorter way of writing the rule
- Final answers should match the notation used throughout the question
How do I know when to use the product rule?
- The product rule is used when we are trying to differentiate the product of two functions
- these can easily be confused with composite functions (see chain rule)
is a composite function, “sin of cos of
”
-
is a product, “sin x times cos
”
- these can easily be confused with composite functions (see chain rule)
How do I use the product rule?
- Make it clear what
and
are
- arranging them in a square can help
- opposite diagonals match up
- arranging them in a square can help
STEP 1
Identify the two functions, and
and
Differentiate both and
and with respect to
with respect to to find
to findformat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%228.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3Eu%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1d67d8ab4f4c10bf22aa353e278%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2216.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3E'%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) and
and format('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%224.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3Ev%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1d67d8ab4f4c10bf22aa353e278%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2212.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3E'%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E)
STEP 2
Obtain  by applying the product rule formula
by applying the product rule formulaformat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%226.5%22%20x2%3D%2226.5%22%20y1%3D%2220.5%22%20y2%3D%2220.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2212.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2220.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3Ey%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2212.5%22%20y%3D%2237%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2220.5%22%20y%3D%2237%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1564b4c0e54101ac57a0cb68c16%22%20font-size%3D%2214%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2237.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2249.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3Eu%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%2256.5%22%20x2%3D%2276.5%22%20y1%3D%2220.5%22%20y2%3D%2220.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2262.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2270.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3Ev%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2262.5%22%20y%3D%2237%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2270.5%22%20y%3D%2237%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1564b4c0e54101ac57a0cb68c16%22%20font-size%3D%2214%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2286.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3E%2B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2297.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3Ev%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%22104.5%22%20x2%3D%22124.5%22%20y1%3D%2220.5%22%20y2%3D%2220.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22110.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22118.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3Eu%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22110.5%22%20y%3D%2237%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22118.5%22%20y%3D%2237%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E)
Simplify the answer if straightforward to do so or if the question requires a particular form
- In trickier problems chain rule may have to be used when finding
and
Exam Tip
- Use
and
for the elements of product rule
- lay them out in a 'square' (imagine a 2x2 grid)
- those that are paired together are then on opposite diagonals (
and
,
and
)
- For trickier functions chain rule may be required inside product rule
- i.e. chain rule may be needed to differentiate
and
- i.e. chain rule may be needed to differentiate
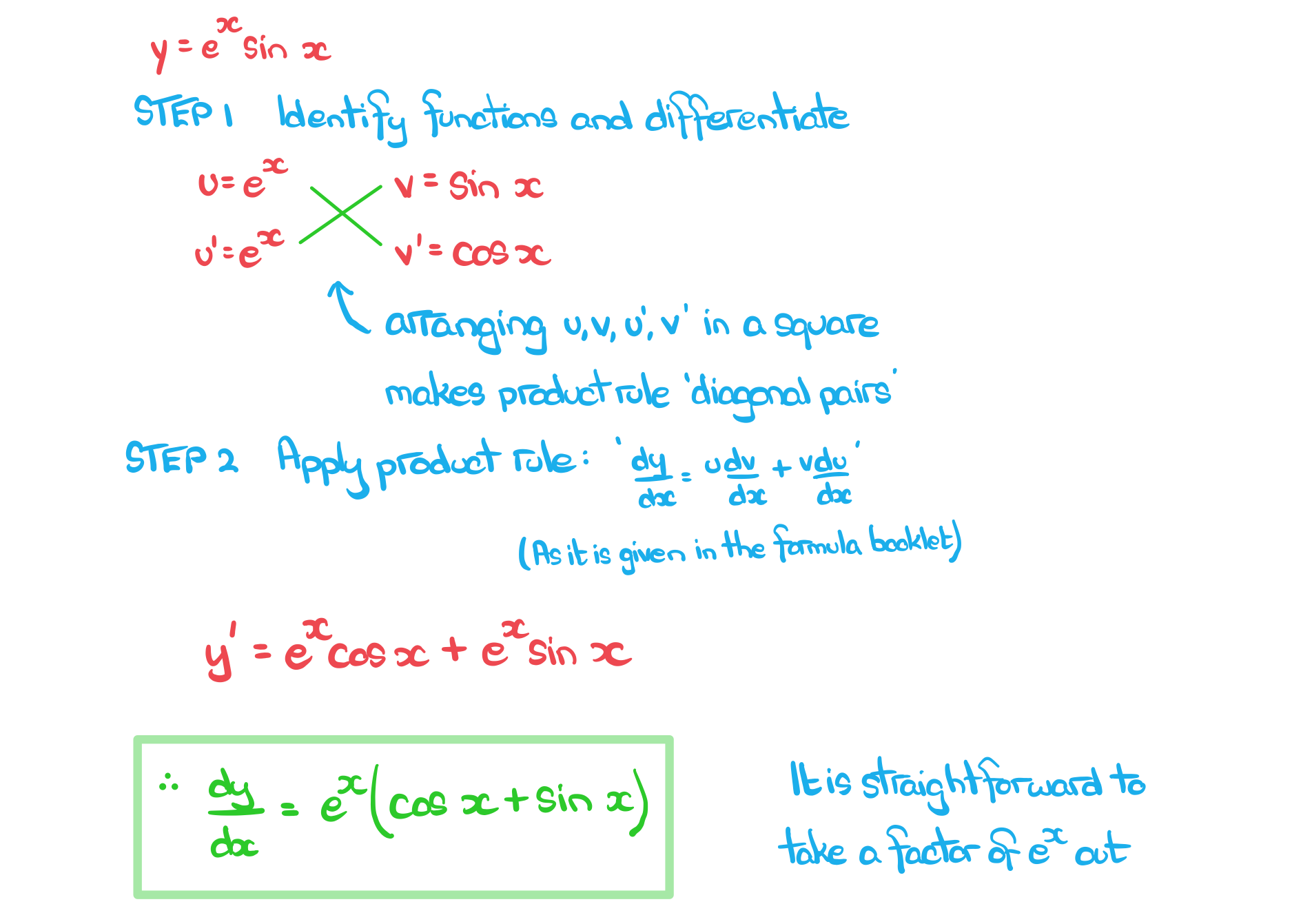
Worked example
a) Find the derivative offormat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%228.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3Ey%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math17f39f8317fbdb1988ef4c628eb%22%20font-size%3D%2214%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2221.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2232.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3Ee%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2240.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2254.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3Esin%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2272.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) .
.
b) Find the derivative offormat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%228.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3Ey%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math17f39f8317fbdb1988ef4c628eb%22%20font-size%3D%2214%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2221.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2233.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3E5%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2241.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2250.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3E2%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2268.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3Ecos%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2287.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3E3%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2295.5%22%20y%3D%2220%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22104.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3E2%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) .
.

Quotient Rule
What is the quotient rule?
- The quotient rule states if
is the quotient
then
-
- This is given in the formula booklet
- In function notation this could be written
- As with product rule, ‘dash notation’ may be used
- Final answers should match the notation used throughout the question
How do I know when to use the quotient rule?
- The quotient rule is used when trying to differentiate a fraction where both the numerator and denominator are functions of
- if the numerator is a constant, negative powers can be used
- if the denominator is a constant, treat it as a factor of the expression
How do I use the quotient rule?
- Make it clear what
and
are
- arranging them in a square can help
- opposite diagonals match up (like they do for product rule)
- arranging them in a square can help
STEP 1
Identify the two functions, and
and
Differentiate both and
and with respect to
with respect to to find
to findformat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%228.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3Eu%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1d67d8ab4f4c10bf22aa353e278%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2216.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3E'%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E) and
andformat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%228.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3Ev%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math1d67d8ab4f4c10bf22aa353e278%22%20font-size%3D%2218%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2216.5%22%20y%3D%2218%22%3E'%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E)
STEP 2
Obtain  by applying the quotient rule formula
by applying the quotient rule formulaformat('truetype')%3Bfont-weight%3Anormal%3Bfont-style%3Anormal%3B%7D%3C%2Fstyle%3E%3C%2Fdefs%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%226.5%22%20x2%3D%2226.5%22%20y1%3D%2242.5%22%20y2%3D%2242.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2212.5%22%20y%3D%2237%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2220.5%22%20y%3D%2237%22%3Ey%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2212.5%22%20y%3D%2259%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2220.5%22%20y%3D%2259%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math143f4d31b04031e49f5eb18baba%22%20font-size%3D%2214%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2237.5%22%20y%3D%2249%22%3E%3D%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%2247.5%22%20x2%3D%22132.5%22%20y1%3D%2242.5%22%20y2%3D%2242.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2253.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3Ev%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%2260.5%22%20x2%3D%2280.5%22%20y1%3D%2220.5%22%20y2%3D%2220.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2266.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2274.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3Eu%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2266.5%22%20y%3D%2237%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2274.5%22%20y%3D%2237%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22math143f4d31b04031e49f5eb18baba%22%20font-size%3D%2214%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2290.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3E%26%23x2212%3B%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22101.5%22%20y%3D%2227%22%3Eu%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Cline%20stroke%3D%22%23000000%22%20stroke-linecap%3D%22square%22%20stroke-width%3D%221%22%20x1%3D%22108.5%22%20x2%3D%22128.5%22%20y1%3D%2220.5%22%20y2%3D%2220.5%22%2F%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22114.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22122.5%22%20y%3D%2215%22%3Ev%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22114.5%22%20y%3D%2237%22%3Ed%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%22122.5%22%20y%3D%2237%22%3Ex%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20font-style%3D%22italic%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2286.5%22%20y%3D%2264%22%3Ev%3C%2Ftext%3E%3Ctext%20font-family%3D%22Times%20New%20Roman%22%20font-size%3D%2216%22%20text-anchor%3D%22middle%22%20x%3D%2295.5%22%20y%3D%2259%22%3E2%3C%2Ftext%3E%3C%2Fsvg%3E)
Be careful using the formula – because of the minus sign in the numerator, the order of the functions is important
Simplify the answer if straightforward or if the question requires a particular form
- In trickier problems chain rule may have to be used when finding
and
,
Exam Tip
- Use
and
for the elements of quotient rule
- lay them out in a 'square' (imagine a 2x2 grid)
- those that are paired together are then on opposite diagonals (
and
,
and
)
- Look out for functions of the form
- These can be differentiated using a combination of chain rule and product rule
(it would be good practice to try!) - ... but it can also be seen as a quotient rule question in disguise
- ... and vice versa!
- A quotient could be seen as a product by rewriting the denominator as
- A quotient could be seen as a product by rewriting the denominator as
- These can be differentiated using a combination of chain rule and product rule
Worked example
Differentiate with respect to
.


You've read 0 of your 0 free revision notes
Get unlimited access
to absolutely everything:
- Downloadable PDFs
- Unlimited Revision Notes
- Topic Questions
- Past Papers
- Model Answers
- Videos (Maths and Science)
Did this page help you?
